Test One - Body movements Flashcards
Goal of Neuromuscular
1-recognizing and interpreting postural patters
2-developing therapeutic and educational strategies to arrest
3-correct and/or improve these debilitation conditions
neuromuscular Techique
A type of deep tissue bodywork using neuromuscular techniques that produces lasting postural change by affecting muscle and nerve to promote homeostasis in CNS
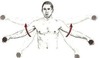
Posture
the attitude of the body
3 cardinal planes
1-longitudinal/saggital
2-frontal/coronal
3-horizontal/transverse
Neuromuscular Warm Up Techniques
The C
The S
Skin Rolling Pinch/Pull
Single Point Pressure
Point to Point Pressure
Cross Fiber/Latitudinal Stroke
Longitudinal Stroke Duck Bill Pinch
The C
With thumb ends touching, push forward with thumbs, while simultaneously pulling back with fingers of both hands, creating a C in the skin. Hold until you feel a release, approximately 10-90 seconds.
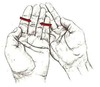
The S
With hands close together, push with one hand on one side and pull with the other, creating an S in the skin. Hold until you feel a release, about 10-90 seconds
Skin Rolling
grip the skin and fascia and pull up and away, slowly moving fingers and thumbs to roll the area, freeing fascia and muscles to allow blood flow.
Pinch/Pull
grip between thumbs and fingers of the skin and fascia, pulling up and away from the body. Hold until you feel a release.
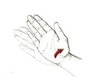
Single Point Pressure
Pressure on one point and hold.
Point to Point Pressure
Apply SPP repeatedly along the length of the muscle.
Cross Fiber/Latitudinal
Stroke across the fibers of the muscle sideways.
Longitudinal
Muscle stripping along the length of the muscle fibers.
Duck Bill Pinch
Pressing a muscle between thumb and fingers.
OT (Optimum Therapy) Zone
varies person to person and varies with each person session to session on a pain scale of 1-10 go for 7-8
Causes of Postural Imbalance
1-Ischemia
2-Trigger Point
3-Nerve Compression & Entrapment
4-Postural Distortion
5-Biomechanical Dysfunction
Palpation allow us to:
1-Locate a structure
2-Become aware of characteristics
3-Assess its quality or condition so you can determine how to treat it.
How to palpate
1-Move slowly
2-Avoid using excessive pressure
3-Focus your awareness on what you are feeling - be present
Proper order to insure the fastest possible recovery without reinjure.
1-Eliminate spasms - massage and NMT reduce spasms
2-Restore proper biomechanics - Active and passive ROM
3-Restore flexibility - stretching the tissues
4-Rebuild strength - exercise injured tissues with light weights
5-Build endurance - conditioning exercises with increasing weights

Supination of Forearm

Inversion of Ankle

Lateral Deviation of Mandible

Posterior Tilt of Pelvis

Rotation of Spine