Taste and Smell Flashcards
what is ageusia?
loss of taset
describe taste innervation of the tongue
Facial nerve (CNVII)- provides fibers to anteriro 2/3
Glossopharyngeal nerev (CNIX)- provides fibres to the posteriro third of the tongue
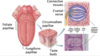
what is the most common of the 3 tastes buds and where is it most commonly found?
circumvallate taste buds
50%
rear if the tongue
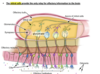
what is the role of taste hairs?
finger like projections of taste cells
contain taste receptors that interact with chemicasl
coverge in taste pore opening
entry point for chemcials in saliva
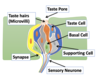
what is the role of a taset cell
To transduce chemical signal into action potential down the sensory neruone (CN7 2/3 ant, CNIX 1/3 post)
what is the role of gustation?

do different atste types have different trhesholds
YES
noxius ( strychinnine hydrocloride)- low threhsold proyective
glucuose- high threshold- takes higher conc for brain to itnerept the sweet takse- protective emchsansim we need ALOT of glucose

what is the role of saliva in taste

what type of tastes have ion channel coupled receptor?
which have G protein coupled?
what happens whent the tastants bind?
Salt and acid (small)- ion channel coupled - Salt Na + enter, acid H+ enter
sweet , biutter umami - G protein coupled (secondary messenger)
Binding casues depolarsition—-> Ca2+ channels open—–> NT exoytosis - synapse with primary senory nerve (CN)
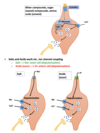
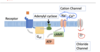
what is labeled here?
describe the taste trasnduction pathway?
- Tongue Cranial nerves
- Solitary nucleus in medulla oblongata (first synapse)
- nucleus of the solitary tract NTS—–>
- thalmic nucleus (ventral posteriro medial nucleus—>
- gustatory cortex in the insular cortex
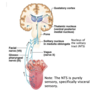
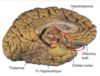
what is this

2 olfactory nerves
where are the olfactory receptors found?
olfactory neurone —> olfactory cilia
cilia extend from apical surface
(rapid turnover olf olfactory neuroen 30-60 days)
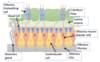
what is the role of the bowmans gland in the mucosa of the nose?

what is the role of the olfactory unsheathing cells
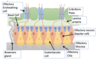
rapidly clear debris (phagocytose axonal debris/dead cells)
protect the neurones
secrete neurotrophic in the olfactory bulbs in the nasal mucosa environment (support growth, survival and differentiation of neurones)