Neuroimaging Flashcards
(18 cards)
rank in order attenuation/ desnity of the materials on CT
bone, air, csf, fat, air, calcificvation

describe what we would see on a CT scan of a patient with vascualr white matter damage and brain atrophy?
braining atrophy- shrinking waay
more CSF- more spaces sbteween brain and the skull, larger areas of ventrciles and deeper sulci

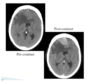
what are we seeing here?


What is the role of contrast in Ct scan
Injectabtkle dye contrast
see the vasculature (blood brain barrier is intact or not)
if the BBB is broke- contrast will leak into tissues and block xray- see more brightly
Tumours etc do not have intact bbb ( so we can see tem with contrast)
what are the cons of CT for brains can

What 2 majro components of soft tissues are ubiquitois with H+, that we take advatnage of in MRI
water and fat
MRI- itneraction between H+ atom(protons), magnetic field and applied Electromagenetic field
MRI gives image of pronton density
so we can see differences in water contetn of CSF, white and grey matter
how does fluid structures show up differenty on T2 vs T1 weight MRI
T2- fluid - white (helpful to detetc oedema)
T1- fluid is darker, greater for contrast between grey and white matter

What structural changes would we see in AD Brain scan
geenral rbain atrophy- -larger gaps around outside of brain
suli and ventricles larger
Atrophy of Meedial temporal lobe (hippocomapsus)- replaced by CSF

how can we use contrast (gadolinium cpmplex) to show glioblatoma on a brain scan?
T1 weighted scan
the contrast agent accumuclates in the tissue

What is an Mr angiography used for
blood flow in the major vessels
weight scan so senstivie to only moving water

what type of weighted scan is usueful in acute stroke?
MRI diffusion weight imaging - detect acute ishaemia
can see change in how water is held in the cell

What is a PET scan
positron emsiision tomography
tissue distributed measured (decay)- whre the trace accumulares
commonly radioactive sugar-Fluorodeoxyglucose (18FDG)
the more energy a tissue uses- the more it takes up the sugar but cannot use it - radioactive decay imates positorns
Tumours- hyper metabolism
Neurodegernation- lack of functional activity

what type of tracer can be used for lzihemeris disease
Pittsburgh compound B-amyloid marker
binds to amyloid plaques in the brain

what can we use in PEt scan to detetc parkinsosn disease
Fluroinated L-dopa
damage to the putamen (striatum)- less uptake of dopamine from the SN

PET vs SPECT?
PET better resoltuion but half-life of tracrs shorter- so need to be made locally- expensiev
what type of scan is this

SPECT- dopamine transporter
what are the short comings of EEG?
blinking, heartbeats
cranila muscle activity
what are the pros of EEG
non invasive
provide excelelnt temporal reolsution (no spatial reosltion because no structural image is porduced


