Systems Pathology: Liver Failure Flashcards
Causes of pre-hepatic jaundice
- Usually anything causing increased RBC destruction
- Unconjugated Bilrubin
- Most Bilrubinn comes from Haem in RBC
RBC membrane related issues in pre-hepatic jaundice
Genetic - Heriditary Speherocytosis (RBC membrane abnormal and unstable - prone to haemolysis so large turn-over of RBCs)
Acquired - Autoimmune heamolotyic anaemia
- Blood group incompatability in blood transfusion
RBC cytoplasm related issues in pre-hepatic jaundice
Genetic - G6PDH deficiency causes RBCs to be unstable
- Haemaglobinopathies; sickle cell, Thalassemia
Acquired: Malaria get into RBC and make it unstable
Causes of hepatic jaundice
- Conjugated plus unconjugated Bilrubin
- Due to abnormality in Liver
Congenital causes of hepatic jaundice
- Immaturity of liver enzymes - prematurity
- Enzyme defects in processing of Bilirubin e.g. Criglar Najar, Gilbert’s
Acquired causes of hepatic jaundice
Viral Hepatitis, Acohol hepatitis
Cause of Post-Hepatic jaundice
Conjugated bilrubin
Obstruction to bile flow e.g. gall stone
Congenital and acquired causes of post-hepatic jaundice
Cong: Biliary Atresia
Acq: Bile duct problem
- Lumen: gall stone, tumuour, worm
- In wall: tumour, bening structure(fibrosis)
- Outside wall: tumour
2 main pathways leading to Acute liver failure

Specific causes of acute liver failure
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Paracetamol overdose
- Viral hepatitis(A, B, E)
- Idiosyncratic response to medication e.g. statins
- Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Features of liver failure
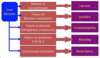
Classification of Chronic hepatitis by causation
- Hep B, C and D
- Autoimmune
- Drugs
- Metabolic disease
- a1antitrypsin deficiency
- Wilson’s disease
Signs/pathology in chronic hepatitis
- Liver necrosis and inflammation
- Portal tracts, periportal hepatocyte, bridging between portal tracts
- Fibrosis
- Portal expansion, periportal, bridges between portal tracts
Which feature is assesed in GRADE and STAGE of chronic hepatitis
GRADE: severity of necrosis and inflammation
STAGE: Extent of fibrosis
Pathological feature of cirrhossis
- Fibrosis
- Nodules of regenerated hepatocytes
- Distorted liver architecture
- Final common pathway of chronic liver injury
- Widespread nidules separated by firbours bands
- may be asymptomatic
- Increases portal pressure
Consequences of increased portal pressure (from cirrhosis)
Spelomegaly - consumption of blood cells
Varices - enlarged veins shunting blood past liver to systemic circulation, may bleed
Ascites - fluid in abdominal cavity
Complications of Cirrhosis
- Variceal haemorrhage
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
- Hepatic encephalopathy
- Chronic liver failure
- Hepatocellular carcinoma


