Syndromes Flashcards
Normal birth, no obvious defects. Developmental delay, seizures, stiff and jerky gait,happy demeaner, easily excitable, hhpermotoric behavior, hand-flapping movements, and short attention span.
Angelman Syndrome
syndactyky (digital infusion) involving second, third and fourth digits, (craniosyntosis) smaller anterior-posterior skull in diameter, flat frontal and occipital bones, high forhead, increased intracranial pressure, midfacial hypoplasia, arched and grooved hard palate, conductive hearing loss, class III malocclusion, thickened alveolar process, long or thickened palate, cleft of the harf palate.
Communication problems: hyponasality, forward carriage of the tongue, artic disorders involving alveolars and labeodental sounds some have normal intelligience.
Apert Syndrome

Caused by spontaneous autosomal dominant mutations, Locus id FGR2 at 10q25-26
Apert Syndrome
caused by dupilcation of chromosome 15.
Angelman Syndrome

high pitched cry resembling cat or infant. Low set ears, narrow oral cavity, laryngeal hypoplasia, microcephaly, hyertelorims, micrognathia, oral clefts.
Communication problems: artic and language disorders typically involving intellectual disability.
Cri du Chat

Caused by absence of short arm of 5th chromosome
Cri du chat
Craniosynostosis, hypoplasia of midface, maxilla or both, hypertelorism, prostrusion of eyeballs, strabismus, parrotlike nose, facial assymetry, tall forhead, malocclusion class III, highly arched palate, shallow oropharunz, long and thick soft palate and brachycephaly (short head).
Communication problems include conductive hearing loss, artic, abnormalities of the palate, hyponasality, and language disorders.
Crouzon
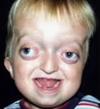
Caused by autosomal dominant inheritance with varied expression in individuals.
Crouzon
generalized hypotonia, flat facial profile, small ears, nose, and chin, and brachycephaly, shortened oral and phayngeal structures, narrow and high arched palate, large tongue, short neck.
communication problems: conductive loss, some sensorineural, language delays and disorders, hypernasality and nasal emission, articl.
Down Syndrome

Caused by extra chromosome 21.
Down Syndrome
Leading inhertited cause of intellectual disability in males. large, long, and poorly formed pinna, bug jaw, enlarged testes, and high forhead.
Communication problems: jargon, perservation, echolalia, inapproariate langage or talking to oneself, lack of gestures and other neonverbal means of communication that normal accompany speech, voice problems and artic problems. autistic like social deficiences.
Fragile X Syndrome

Caused by expansion of nucleic acid CGG which repeats too often on the fragile X mental retardation gene, located on bottem end of the X chromosome.
Fragile X Syndrome
Most die in early teens or before the age of ten. dwarfism, hunchback, intellectual disability, short and thick bones, low nasal bridge, noisy respiration.
Communication problems: sensorineurall hearing loss, thick, everted lips, large tongue, small malformed teeth, comprimised intellgibility
Hurler’s Syndrome

caused by autosomal recessive deficiency of X-L iduronidase.
Hurler’s Syndrome
Form of aphasia whereby formaly healthly childern ages 3-7 lose their ability to comprehend language and then speak it. Loss can be sudden or gradual. Some regain abilities and have relapses. Some do not. 80% of children affected develop epilepsy.
Landau-Kleffner Syndrome














