Stomach & SI Flashcards
See clinical correlates - Anatomy 4
What does the celiac trunk supply
Foregut & spleen
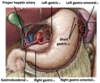
What does the celiac trunk give rise to (3)
- Common hepatic artery
- Splenic artery
- Left gastric artery

What is the parasympathetic innervation of the celiac trunk
Vagus nerve - CN X
What is the sympathetic innervation of the celiac trunk
PRE-GANGLIONIC
Thoracic splanchnic nerves (T5 - T9)
POST-GANGLIONIC CELL BODIES
Celiac ganglion
Name the 2 main branches of the common hepatic artery
Gastroduodenal
Proper hepatic artery
3 branches of the gastroduodenal artery
- R gastro-omental
- Supraduodenal
- Superior pancreaticoduodenal - ant & post
3 branches of the proper hepatic artery
Where does it run
- R gastric
- L hepatic
- R hepatic -> Cystic
Proper hepatic artery runs through the hepatoduodenal ligament - free edge of lesser omentum
3 branches of the splenic artery
Where does it run
- Short gastric
- Left gastric omental
- Dorsal, greater and inferior pancreatic
Runs along superior border of pancreas to spleen
Branch of the left gastric artery
Where does it run
Oesophageal branches
Descends along lesser curvature of stomach
What does the superior mesenteric artery supply
Midgut
What is the parasympathetic innervation of the sup mesenteric a.
Vagus nerve (CN X)
What is the sympathetic innervation of the sup mesenteric a.
PRE-GANGLIONIC
Thoracic splanchnic nerves (T9 - T12)
POST-GANGLIONIC CELL BODIES
Sup mesenteric ganglion
5 branches of the sup mesenteric a.
- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal
- Intestinal
- Middle colic
- Right colic
- Ileocolic

Inf pancreaticoduodenal supplies
Duodenum distal to papillae
Intestinal supplies
Vasa rectae (15-18 branches)
- What does the middle colic form part of
- clinical anastomosis with
- Marginal artery of Drummond
- Inferior mesenteric a.
Right colic supplies
Ascending colon
Ileocolic supplies
Appendicular artery
3 branches of the inferior mesenteric a.
- Left colic
- Sigmoid
- Superior rectal

Parasympathetic innervation of the inferior mesenteric a.
Pelvic splanchnic nerves
Sympathetic innervation of the inferior mesenteric a.
PRE-GANGLIONIC
Lumbar splanchnic nerves (L1-L2)
POST-GANGLIONIC CELL BODIES
Inferior mesenteric ganglion
What does the left colic form part of
Clinical anastomosis with
Marginal artery of Drummond
Superior mesenteric a.
Superior rectal supplies
Proximal 2/3rds of rectum
(terminal branch)
Anterior view of the supracolic viscera ex situ, with the lesser omentum removed