Steroid Biosynthesis Staudinger Flashcards

-Streak ovaries because the chromosomal analysis revealed a karyotype of 45,XO which is diagnostic of Turner syndrone.
they have normal intelligence, individuals bor with downs have macroglossia, edwards syndrome patients have micrognathia, patau syndrome would have cystic kidneys
Adrenal hyperplasia is caused by what?
deficiencies in the adrenal enzymes that are used to synthesize glucocorticoids
Hirsutism:
excessive body hair in men and women on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal
General oligomenorrhea: can be a symptom of what?
adrenal hyperplasia
infrequent menses
How would you tell if a fetus was at risk for congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
determined using human leukocyte antigen haplotype
demonstration of excess cortisol precursors in amniotic fluid

Answer A is incorrect because 17-hydroxylase deficiency presents in males with ambiguous genitalia due to decreased test. production
b wrong because would present w/ low blood pressure and elevated test
c wrong because its the opposite
d converts thyroid hormone T4 to T3 and isnt part of the adrenal steroid axis

Biochemistry of adrenal hyperplasia
what is result of a 21-hydroxylase (Cyp21A2) deficiency?
what is the result of a 11-BHydroxylase (Cyp11B1) deficiency?
-accumulation of progesterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone if 21-hydroxylase deficient
accumulation of 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol if 11-B hydroxylase is deficient

Conn syndrome
\

Desmolase
where is it at
- action
- whats it regulated by
- where is regulator produced?
adrenal cortex enzyme that produces pregnenolone from cholesterol.
regulated by ACTH, which is made in Ant. Pit
Biology of ACTH
- how many aa
- stimulates what, which does what?
how is this all regulated?

ACTH:
where in the adrenal cortex?
what are ACTH receptors?

Normal biochemistry of ACTH
- upon ligand binding what happens?
- what happens in tumor?
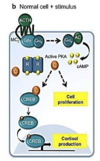
upon ligand binding the receptor undergoes confromation changes that stimulate the enzyme adenylyl cyclase, which leads to an increase in intracellular cAMP and subsequent activation of protein kinase A
in tumor, pka is not dependent on acth, its always on
P450scc enzyme
where is it located, what does it do?

what type of circuit is ACTH on mitochondrial enzymes
“feed forward”
17,20 Lyase (CYP17A1)
- where does the protein localize, what activity does it have
- key enzyme in which pathway
- mutations produce what?


Cholecalciferol (d3)

How is Vitamin D3 obtained (two ways)
- reaction that occurs in the liver makes what? which CYP?
- reaction that occurs in the Kidney produces what? which enzyme?
CYP2R1 converts cholecalciferol to 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol



