Immunology Mechanisms of Diabetes Flashcards
Changes in the concept of T2D
past
present
in the past it was thought obesity led to insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia, now it is undersootd that beta cell loss leads to reduced beta cell mass and a reduced insulin secretion. So now its insulin resistance and at later stages a low production
Genetics of T2D
how do you know its genetic and environmental?
what population has strangely high risk
- know its genetic because offspring of parent has 40% chance, if both parents have it, there is a 70 percent chance.
- concordance rate of T2D was 34% among MZ twins and 16% of fraternal, suggests significant environtmental role
pima indians have 10 fold higher prevalence than general US population
environmental: sedentary/high fat lifestyles, studies have shown pollution and exposure to organic land pollutants induces insulin resistance.
- traffic related pollutants (particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, is associated with higher risk of t2d)
In a normal individual how does insulin sensitivity work?
- affect on glucose uptake, fatty acid release, hepatic gluconeogenesis
- what do adipose tissue macrophages and Kupffer cells express? suppress?
- overall serological state?

what happens in insulin resistance? (general mechanism)
inflammation leads to beta cell death
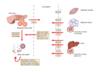
What type of macrophages dominate in lean vs obese person?

Lean conditions:
what do adipocytes secrete?
promotes activation of what?
why is this important?

obesity conditions:
adipocyte changes result in increased what?
what do the adipocytes release?
why is this important?

Palmitate-TLR4 pathway:
what is palmitate?
Beta cells sense palmitate how?
what do the beta cells recruit?
end result?

What is Type 1 Diabetes?
- characterized by?
- ketoacidosis?
- HLA associations and autoantibody
- mediated by what kind of cell?
- what is insulitis? caused by?

Genetics of Type 1 Diabetes:
Familial clustering?
before 20 years old?
concordance (MZ vs DZ)

what genes are associated with T1D
- HLA?
- insulin gene, mechanism, chromosome #
- regulators, expression location
- CTLA-4, roll

How is central tolerance to insulin established?

Role of HLA in T1D:
high risk allelles?
most common heterozygous genotypes in children
Asp57?
which class II haplotypes confer dominant protection?

The Insulin Gene (IDDM2)
- where is the VNTR located?
- Classes
- which class are susceptible?
- what happens to central tolerance?

Transcriptional AutoImmune Regulator (AIRE)
- what does it control?
- malfunction of AIRE leads to?
- Critical for what?
























