SPO6: Plant Diversity III Flashcards
Plant tissue systems (groups) (3)
- Dermal
- Vascular
- Ground
Tissues on the surface of the plant, usually 1 cell thick and covered by a waxy cuticle. The interface between the plant and the environment.
Dermal tissue
Tissues that distribute water and nutrients. (2)
Vascular tissues, including Xylem and Phloem
1
Transport of water and minerals, support. Composed of tracheids and vessel (cells) elemtents

Xylem
4
Transport of photosynthetic products. Composed of sieve tube elements (Cells) with sieve plates.

Phloem
Tissues beneath the dermal tissues and surrounding the vascular tissues.
Name the different types of cells associated with these tissues (3).
Ground tissue.
- Collenchyma
- Parenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Cells near surface of stem, leaf petioles and veins. Unevenly thickened walls for support in young plants.

Collenchyma cells.

These cells have thick walls usually with lignin for support for mature plants and may be dead at maturity.

Sclerenchyma

Most abundant cell in plants, thin walled, large vacuoles, photosynthetic, support, storage

Parenchyma

Growth from apical meristems. Increases plant linear axis e.g. stem and root length.
PRIMARY GROWTH
Growth from the cambium. Increases girth.
SECONDARY GROWTH
Actively dividing cells in stem buds and root tips. Provide growth in the linear axis of plants.
Primary meristems
Located between the xylem and phloem. Increases girth of plant. A cork ______ is found in woody plants

(Vascular) Cambium
1

Root hairs
2

Zone of differentiation
3

Zone of elongation
4

Zone of cell division
5

Root cap
Cork
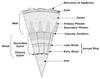
Cortex

Bark

1.

Apical buds
2

Reproductve shoot (Flower)
3

Node




















