SM_215a: Genetic Cystic Kidney Disease Flashcards
_____ is the most common monogenic cause of ESRD worldwide
ADPKD is the most common monogenic cause of ESRD worldwide
ADPKD is due to mutations in _____ and _____, which are functional components of ______
ADPKD is due to mutations in PKD 1 and PKD 2, which are functional components of tubular epithelial cells
PKD1 accounts for _____ cases of ADPKD and is _____ severe
PKD1 accounts for most cases of ADPKD and is more severe
Inheritance of ADPKD is ______
Inheritance of ADPKD is autosomal dominant
(5% due to de novo mutations)
ADPKD exhibits _____ phenotypic variability
ADPKD exhibits significant phenotypic variability
(many mutations in each gene, severity of illness affected by specific mutation, somatic second-hit mutation)
ADPKD is a _____pathy
ADPKD is a ciliopathy
In ADPKD, cAMP _____ and Ca _____, leading to formation of _____
In ADPKD, cAMP increases and Ca decreases, leading to formation of cysts

In ADPKD, increased ADH causes cysts to grow _____
In ADPKD, increased ADH causes cysts to grow faster

In ADPKD, normal kidney tissue is replaced with large cysts, causing _____ and _____
In ADPKD, normal kidney tissue is replaced with large cysts, causing tubular obstruction and RAAS activation

ADPKD causes _____ cysts and _____ enlarged kidneys
ADPKD causes innumerable cysts and bilaterally enlarged kidneys
(cysts variable in size, cysts push normal tissue out of the way)
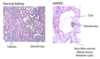
On histology, ADPKD manifests as _____
On histology, ADPKD manifests as very little normal kidney tissue between cysts
In ADPKD, as total kidney volume increases, eGFR _____
In ADPKD, as total kidney volume increases, eGFR decreases
(total kidney volume is a good prognostic factor to predict rate of decline of GFR, a biomarker for ADPKD)

Main extrarenal manifestations of ADPKD are ______ and ______
Main extrarenal manifestations of ADPKD are hepatic cysts and intracranial aneurysms
ARPKD has a _____ severe phenotype than ADPKD
ARPKD has a more severe phenotype than ADPKD

Abnormalities of ARPKD are present in _____ or at _____
Abnormalities of ARPKD are present in utero or at birth
(fetal abnormalities are oligohydramnios, pulmonary hypoplasia, and limb defects)
ARPKD is causes by a genetic mutation in _____, which encodes _____
ARPKD is causes by a genetic mutation in PKHD1 gene, which encodes for fibrocystin
(fibrocystin found in primary cilia of tubular epithelial cells and bile duct epithelial cells)
ARKPD most commonly affects _____, and abnormalities in _____ and _____ occur together
ARKPD most commonly affects children, and abnormalities in kidney and liver occur together
In ARPKD, kidneys become large but _____
In ARPKD, kidneys become large but stabilize in size at some point
(in contrast to ADPKD)
In ARPKD, cysts are _____
In ARPKD, cysts are longitudinal

Extrarenal ARPKD is always associated with _____ and _____, often leading to _____
Extrarenal ARPKD is always associated with biliary dysgenesis and congenital hepatic fibrosis, often leading to portal hypertension
(at risk for cholangitis)
Medullary cystic kidney disease is characterized by histologic evidence of _____
MCKD is characterized by histologic evidence of tubular and interstitial fibrosis
MCKD is associated with _____ urinary abnormalities
MCKD is associated with minimal urinary abnormalities (little proteinuria or hematuria)
(only 50% of patients have cysts)

MCKD is associated with mutations in _____, _____, and _____
MCKD is associated with mutations in MUC1 (encodes mucin 1), UMOD (encodes uromodulin), and REN (encoded renin)
MCKD is commonly associated with _____ and _____
MCKD is commonly associated with hyperuricemia and gout (kidney stones)



