SM MSK Anatomy - Upper Limb: Axilla, Shoulder, Arm, Forearm, Hand Flashcards
SM 222a, Lab 2, Lab 3, Lab 4, Lab 5,
Which nerve might be injured by a fracture of the hook of the hamate?
Which functions would be compromised?
Ulnar nerve
- Finger abduction, adduction would be lost
- Interossei
- Flexion of 3rd-5th MCP, extension of 3rd-5th PIP and DIP would be weakened
- Lumbricals
- Thumb adduction
- Adductor pollicis
- Sensation over the skin of the medial 1.5 fingers, palm, and dorsum
- Cutaneous branches

Damage to which nerve would result in pain or sensory loss on the medial side of the forearm?
Medial cutaneous nerve
Note - if a cutaneous nerve is damaged, there will be no motor loss because it is a cutaneous nerve
(superficial branch of the ulnar nerve)
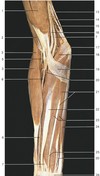
What structure is labeled by #8?

Long head of triceps brachii

This image shows the deepest layer of the anterior compartment of the arm
Which structure is labeled by #40?

Flexor digitorum profundus
(The only muscle that can flex the fingers at the DIP joints!)

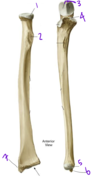
Identify #1:
What muscle attaches to #1?

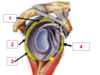
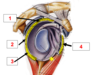
1: Greater tubercle of the humerus
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor attach here

What is the function of the lumbricals of the hand?
What is their innervation?
Radialy deviate the fingers, flex MCP, extend PIP and DIP
Median nerve for 1-2
Ulnar nerve for 3-4
Following a dog bite to the arm, a patient reports a loss of sensation over the 5th digit (pinkie). Cutaneous branches of which nerve may have been injured?
Cutaneous branches of the ulnar nerve
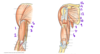
When the arm is abducted 180 degrees, _____ degrees occurs by rotation of the scapula and ______ degrees occurs by rotation of the humerus at the shoulder joint
When the arm is abducted 180 degrees, 60** degrees occurs by rotation of the scapula and **120 degrees occurs by rotation of the humerus at the shoulder joint
The scapula and the humerus move in a 1:2 ratio
What innervates adductor pollicis?
Ulnar nerve
If the median nerve (or recurrent branch of the median nerve) is damaged, the abductor pollicis brevis will no longer work; the thumb will be pressed against the hand by adductor policis
Which muscles protract the scapula?
Serratus anterior
Pectoralis minor
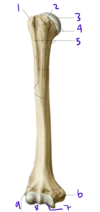
Describe the structure labeled by #3
- Muscle:
- Function:
- Attachments:
- Innervation:

- Muscle: Brachioradialis
- Function: Flex the elbow
- Attachments: Humerus, distal radius
- Innervation: Radial nerve

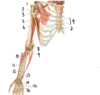
Which vein is labeled by #2?

Cephalic vein
(Empties into the axillary vein)

A man suffering from entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the medial epicondyle gets a medial condylar osteotomy. During the procedure the muscular attachments to the medial epicondyle are accidentally cut. Which of the following muscles may have been damaged?
A) Supinator
B) Flexor carpi radialis
C) Brachioradialis
D) Extensor carpi ulnaris
E) Flexor pollicis longus
B) Flexor carpi radialis
Muscles of the superficial layer of the anterior forearm:
- Pronator teres (Creates the medial border of the cubital fossa)
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris

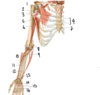
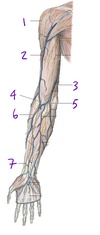
Which structure is labeled by #11?

Ulnar nerve
Travels closely with the ulnar artery (17)

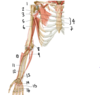
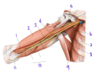
Which nerve supplies the structures in purple (labeled #4)?

Medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm
(A branch from the brachial plexus)

Which structure is labeled by #5?

Head of the ulna
Fig. 11.4 Adapted from Gilroy et al. Atlas of Anatomy, second edition, Figs. 22.1A, 22.1B.

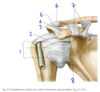
The vessels labeled by #4 most recently originated from which vessel?

Subscapular artery
(Posterior = circumflex scapular artery, anterior = thoracodorsal artery)
Fig. 16.2 Adapted from Gilroy et al. Atlas of Anatomy, second edition, Fig. 24.1B.

Describe the muscle labeled by #6
- Muscle:
- Function:
- Attachments:
- Innervation:

- Muscle: Supinator
- Function: Supinate the forearm
- Attachments: Lateral epicondyle of humerus, radius
- Innervation: Radial nerve

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Surgical neck of the humerus

In the brachial plexus, the medial cord branches into the…
Ulnar and median nerves

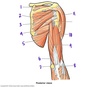
Describe the deltoid muscle
- Function:
- Innervation:
- Attachments
Deltoid
- Function: Arm abduction, flexion, internal rotation
- Innervation: Axiliary nerve (C5-C6)
- Attachments: Clavicle, acromion, scapular spine, humerus
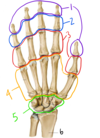
Together, the structures labeled #4 make up the…

Metacarpals
Fig. 11.5 Adapted from Gilroy et al. Atlas of Anatomy, second edition, Fig. 23.2.

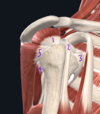
Which structure is labeled by #4?

Coracoacromial ligament

Which structure is labeled by #7?

Pronator quadratus