SM MSK Anatomy - Lower Limb, Femoral Triangle, Glute, Foot, Gait Flashcards
SM 223a, Lab 2, Lab 3, Lab 4, Lab 5
Which structure is labeled by #12?
Function?
Innervation?

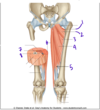
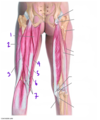
Vastus lateralis
Knee extension (inserts on greater trochanter of femur)
Femoral nerve

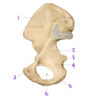
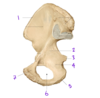
What view of the femur is this?

Posterior view
(You can see the intercondylar notch in between the medial and lateral condyles)
Fig. 56.2 Adapted from Gilroy et al. Atlas of Anatomy, 2nd edition, Figs. 26.4 A, 26.4 B

Which structure is labeled by #12?

Semitendinosus

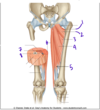
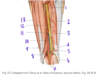
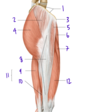
Which muscle is labeled by #4?

Piriformis

Which vessel is most likely to be damaged by a femoral neck fracture?
What is the consequence?
Medial femoral circumflex artery
This can lead to necrosis of the femoral head

Which gait phase is showin in picture 3?
Which muscles are active?

Mid stance
The foot on the ground is supporting the whole weight of the body
- Quadriceps femoris is extending the knee as the body moves over the planted foot
- Gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, an dtensor fascia late are contracting to hold up the hip of the other (swinging) leg

Which structure is labeled by #9?

Semimembranosus

Which nerve supplies the big toe compartment of the foot?
What actions does it control?
Medial plantar nerve (branch of the tibial nerve)
Abduction and flexion of the hallux
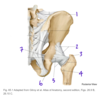
Which structure is indicated by #2?
What is its primary function?

Piriformis
Lateral rotation of the hip

Which structure is labeled by #10?
What is its function?
What are its attachments?

Tibialis posterior
Foot inversion, plantarflexion
Tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane + sole of the foot (tarsals)

What are the components of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial nerve
Common fibular nerve
Hip extensors are found in the _________ compartment of the thigh, and are supplied by the _________ nerve
Hip extensors are found in the posterior** compartment of the thigh, and are supplied by the **tibial (sciatic) nerve
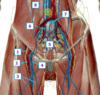
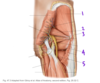
Which structure is labeled by #2?

Inguinal ligament

Which structures are in group A?
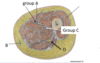
Superficial femoral artery, and vein
Femoral nerve

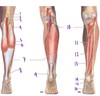
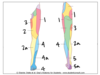
Identify the structures of the lateral compartment of the leg.
What innervates them?

Fibularis longus (5)
Fibularis brevis (6)
Superficial fibular nerve

Which muscles acts to invert the foot?
Tibialis posterior, Tibialis anterior
What are the nerve branches of the lumbo-sacral plexus?
- Obturator
- Femoral
- Superior gluteal
- Inferior gluteal
- Sciatic nerve
- Tibial nerve
- Common fibular nerve
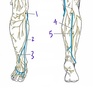
Which structure is labeled by #5?

Tibial nerve

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Tibia

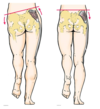
Which nerve supplies the areas indicated in yellow (#2 and #2a)?

2a is supplied by the saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve
Femoral nerve

A physician would like to block cutaneous nerves in order to remove a small subcutaneous lipoma from the medioanterior surface of the thigh. The branches of which nerve should be blocked?
A. sural
B. tibial
C. musculocutaneous
D. femoral
D. femoral
Supplies the anterior surface of the thigh. May also block branches fo the obturator nerve.
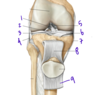
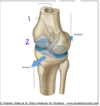
Which structure labels the anterior cruciate ligament?
Which structure labels the posterior cruciate ligament?

Anterior cruciate ligament = #2
Posterior cruciate libament = #1
Which dermatomes are important for making the diagnosis of sciatica?
S1 and S2

Which structure is labeled by #3?

Femoral artery and femoral vein
Fig. 59.7 Adapted from Gilroy et al. Atlas of Anatomy, second edition, Fig. 29.34 B.