SM 228a - Spondyloarthropathies Flashcards
What genetic factor is associated wtih seronegative spondyloarthropathies?
HLA-B27
Which cytokines can be targeted using biologic therpay to treat psoriatic arthritis?
IL-23 (+/- IL-12)
IL-17
TNF
What percentage of psoriasis patients will develop psoriatic arthritis?
~25%
What pattern of articular disease defines seronegative spondyloarthropathies?
Inflammation
- Spine involvement
- Hands: PIP and DIP affected
- MCP spared
- Asymmetric joint involvement
- Enthesitis
What is the typical treatment for patients with seronegative arthritis?
- Anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs)
- Physical therapy
- If NSAIDs fail…
- Corticosteroids
- DMARDS
- Biologics
What are the typical extra-articular manifestations of the seronegative spondyloarthropathies?
Enthesitis
Iritis
Skin (psoriatic), GI (IBD-related)
Which arthritis has both destructive and new-bone changes?
What pattern does this produce?
Psoriatic arthritis
“pencil in cup”

Describe the presentation of ankylosing spondylitis
- Inflammatory back pain and stiffness
- Sacroiliitis
- Oligoarthritis
- Enthesitis
- Systemic symptoms
- Fatigue, imparied sleep
- Extra-articular disease
- Uveitis, IBD, aortitis
- Symptoms begin in 20’s, but diagnosis is often late
List some of the relevant spondyloarthropathies
Spondyloarthropathies = inflammatory, seronegative
- Reactive arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Axial spondyloarthritis
- Arthritis associated with IBD
Describe the clinical presentation of reactive arthritis
- Acute inflammatory arthritis
- Involves only a few joints
- Follows GI or GU infection
- Usually self-limited
- May be recurrent or chronic
What is spondyloarthritis?
A specific group of inflammatory arthritides that share some common elements
- Sero-Negative (negative for RF)
- Spine involvement
- Enthesitis
- Genetic markers
- Asymmetric joint involvement
- Iritis
- No female predominance
How can you distinguish between rheumatoid arthritis and reactive arthritis?
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- More likely to be RF positive
- MCP affected
- DIP spared
- Female predominance
- Reactive arthritis
- Asymmetric
- DIP and PIP affected
- No female predominance
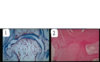
Which picture shows osteoarthritis?
Which one shows inflammatory?
How do you know?

- 1 = ostoarthritis
- No hypercellularity
- Cartilage erosion
- New bone formation
- No bone erosions
- 2 = inflammatory arthritis
- Hypercellularity in the synovium
- Bone erosion
Describe the pathophysiology of reactive arthritis
Previous infection can trigger an inflammatory reaction
- This is not an ongoing infection
- Must treat the inflammation - treating the microbe doesn’t work
These nail changes are characteristic of which kind of arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis
A “Pencil in cup” feature of a joint is pathopneumonic for which arthritis?

Psoriatic arthritis
Requires both erosion and new bone formation
(psoriatic arthritis is the only arthritis that has both destrictive and new bone changes)
What infections can trigger reactive arthritis?
- Enteric infections
- Shigella, salmonella, yersinia, campylobacter, clostridium
- Urogenital infection
- Chlamydia
Causative agent may be asymptomatic!
May be a genetic predispostion (HLA-B27) in addition to previous infection
Which spondyloarthritides are classically “axial?” Which are classically “peripheral”?
- Axial
- Axial spondyloarthritis (ankylosing spondylitis is a subset)
- Peripheral
- Psoriatic arthritis
IBD arthritis, reactive arthritis are more in the middle
What is the significance of HLA-B27 in reactive arthritis?
Some HLA-B27 subtypes may have an amino acid sequence homology with some infectious agents
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Shigella flexneri
- Klebsiella
Infection by these agents triggers the immune system ot attack its own HLA-B27
Rats with high levels of HLA-B27 developed reactive arthritis spontaneously
What is inflammatory enthesopathy?
Subchondral bone inflammation and resorption at the insertion of tendons
Periosteal new bone formation (not just calcification of the tendon)

Describe the clinical features of psoriasis arthritis
- Cutaneous disease
- Psoriatic plaques
- Onycholysis and nail pitting
- Skin disease usually (90%) precedes joint involvement
- Inflammatory polyarthritis
- Asymmetric or symmetric
- DIP and PIP, MCP spared
(MCP usually involved in RA)
- DIP and PIP, MCP spared
- Axial
- Asymmetric or symmetric
- Dactylitis
- Enthesitis
- RF negative
Psoriatic arthritis is a spondyloarthritis
Describe the articular features of reactive arthritis
- Additive
- Asymmetric
- Mono or oligo arthritis
- More commonly affects large lower extremity joints
- Dactylitis
- Enthesitis
- Inflammatory lower back pain
Which feature is shown in this radiograph?
Which arthritis is it characteristic of?

Bamboo spine
Due to ossification of the outer layers of the annulus fibrosis
Note: no osteophytes, which are characteristic of osteoarthritis


