SM MSK Anatomy - Back and Spine Flashcards
SM 221a, Lab 1
What are the functions of the intrinsic back muscles?
Move the vertebral column
Extension, lateral bend, rotation
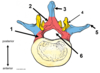
Which structure is labeled by #3?

Vertebral foramen
(Spinal cord runs through here)

The intrinsic muscles of the back attach to the ______
The intrinsic muscles of the back attach to the vertebral column
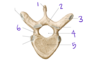
Identify the follwing on both the MRI and the bone
- Vertebral body
- Vertebral foramen
- Spinous process

https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224950784_Unexpected_neuroimaging_abnormalities_in_patients_with_apparent_C8_radiculopathy_Broadening_the_clinical_spectrum/figures?lo=1

How many sacral vertebrae are there?
4-5
Which structure is indicated by #2?

Nucleus Pulposus
Gelatinous remnant of the embryonic notochord

True or false?
Back muscles attaching to the scapula will receive innervation from dorsal rami of the appropriate thoracic level
False
- Back muscles attaching to the scapula are extrinsic muscles
- They are innervated by ventral rami
- Except trapezius, which is innervated by CN XI (the spinal accessory)
Where could this portion of spinal cord be taken from?

T1 through L1
Spinal nerves do not originate from cervical vertebrae
(cranial nerves exit cervical vertebrae)
The spinal cord ends at L1. The cauda equina takes spinal roots down to the lumbar and sacral vertebrae, where they exit as spinal nerves
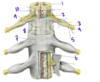
What are the 3 groups of intrinsic muscles of the back?
(From superficial to deep)
- Splenius
- Erector spinae
- Transversospinalis
What structure is labeled by #5?

Spinal nerve
Emerges from the vertebral column through the intervertebral foramen

True or False?
The iliocostalis and the splenius are both extensors of the spine
True
- Iliocostalis extends the lumbar and thoracic regions
- Part of the erector spinae
- Splenius extends the head and neck
- All intrinsic back muscles function as extensors

Which structure is labeled by #2?

Lamina (part of vertebral arch)

Which structure attaches the pia mater to the coccyx?
Filum terminale

What is inside of the dural sac at the level of L3?
Cauda equina + arachnoid mater
The spinal cord ends at L1, giving rise to spinal roots that bundle together to form the cauda equina
Which structure is labeled by #4?

Spinous process

Which structure is labeled by #6?

Vertebral foramen
(This is where the spinal cord would be)

What are the most common sites for herniated discs?
Between L4-L5 in the lumbar region -> lower back/leg pain
May also occur in the cervical region -> neck/arm pain
Which structures hold the vertebrae together?
Ligaments and vertebral disks
What structure is labeled by #1?

Scapular spine

Which muscle is indicated by #1?
What is its function?
Attachments?
Innervation?

- Muscle: Serratus posterior superior
- Thin sheet of muscle underneath the trapezius and rhomoboids
- Poorly developed
- Function: Nobody knows!
- Possible accessory respiratory function
- Attachments: Ribs, spinous process
- Innervation: Ventral rami of spinal nerves

Which structure is labeled by #1?

Pedicle

Which structures make up the vertebral arch?
Lamina + pedicle

While stopped at a light, a man’s car is rear-ended at high speed. He is brought to the emergency room with difficulty breathing and a severe hyperextension neck injury. His MRI shows a rupture of the anterior annulus of C4-5 intervertebral disc, inflammation of the disc, and a preverterbal hematoma (the cause of his breathing difficulty). Which of the following ligaments was likely disrupted?
- Anterior longitudinal
- Ligamentum flavum
- Interspinous
- Supraspinous
- Posterior longitudinal

a. Anterior longitudinal
Often injured in whiplash injuries
This is an axial T2 MRI of the lumbar spine
How is the muscle group outlined in red innervated?

Dorsal rami of the spinal nerves
These are intrinsic back muscles