Skin Infections Flashcards
How is the skin the first line of defense against microbial pathogens ?
- It is a physical barrier 2. Secrets a low pH sebacous fluid and fatty acids as well as antimicrobial peptides to inhibit growth of pathogens. 3.By possessing its own normal flora, it prevents the colonization of other flora
What are the steps to bacterial colonization ?
- Invasion- normally through a break in the skin 2. Interaction between the bacteria and the host tissue causes the clinical effects.
What are the three steps of disease pathogenesis once the bacteria has invaded the skin ?
- Bacterial adherence to host cells 2. Invasion of tissue with evasion of host defenses 3. Elaboration of toxins
What are the two main classes of toxins and how do they cause damage ?
Exotoxins are actively secreted proteins that cause tissue damage or dysfunction through various mechanisms. Endotoins
What are super antigens ?
Usually made by S. Areus and S. Pyrogenes. These are a group of exotoxins that cause a massive release of cytokines that grossly exaggerates inflammatory responses.
What is Impetigo ?
Superficial crusting epidermal skin infection that presents in bullous and nonbullous forms.
Who usually gets impetigo ?
children and it usually infects the face. Caused by both S. Areus and S. Pyogenes. The characteristic feature is a honey colored crust.
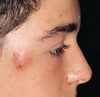
What is Erysipelas ?
It is a streptococcal infection of the superficial dermal lymphatics that demonstrates sharply demarcated and raised borders. **Picture was inflammation with above described manifestation over the entire orbital bone
What is cellulitis ?
It is an infection of the deeper dermis and sub-q with poorly demarcated borders. The vast majority are streptococcal in origin.
What is a cutaneous abscess ?
A collection of pus in the dermis and sub-q tissue
What is folliculitis ?
A superficial infection of the hair follicle with a collection of pus in the epidermis.
What is a furuncle ?
A boil with a deeper involvement of the particle. The infection extends into the sub-q tissue
What is a carbuncle ?
Numerous furuncles coalesce to form a single inflamed area.
Diffuse generalized arrhythmia and superficial desquamation with flexural accentuation. Mucous membranes are uninvolved. There is perioral and periocular crusting and radial fissuring with mild facial swelling
Staph scalded skin syndrome. IT will present primarily in infants or adults with renal failure. There will be granular splits in the dermis that lacks inflammatory infiltrate.
What is necrotizing fasciitis ?
NF is an insidious and deadly soft tissue infection characterized by widespread tissue necrosis. MUCH DEEPER PLANE THAN CELLULITIS
Type 1 Necrotizing Fasci
Polymicrobial
Type 2 NF
Strep flesh eating
Type 3 NF
Clostridial Myonecrosis- Gas Gangrene
How could you know you have NF ?
Pain that is much worse than the clinical findings. Exquisite tenderness and erythema, warmth and swelling. -Skin changes from red and purple to gray blue within 36 hours.
What happens if you delay NF diagnosis-
Fatal
What causes Toxic shock syndrome ?
TSST-1 Toxin which is released by S. Areus **Surgery Deep abscesses and Tampons
What are the clinical features of toxic shock syndrome ?
Fever, strawberry tongue, sunburn like erythema and sandpaper papules. Later causes desquamation. You must remove the focus of infection and give ABX
What produces periorfical abscesses ?
Anarobic organisms
What organism produces pus ?
Staph Areus