Skin and Soft Tissue Infections Flashcards
What bacteria like to live in areas with less aciditic pH?
- S. Aureus
- S. Pyogenes
What is pictured here?

Impetigo


Describe impetigo?
- Gold crusty lesions in dermis
- Mostly in children
- Cauesed by S. Aureus
What is the treatment for Impetigo?
- Usually self-limiting
- Topical fusidic acid
- Systemic antibiotics if required
What is pictured here?

Tinea
Describe Tinea?
- Fungal infection of skin/nails
- Diagnosis made on skin scrapings
What are the most common causes of Tinea?
- Microsporum
- Trichophyton
- Epidermophyton
What is the treatment for Tinea?
- Terbinfine cream
- Terbinafine or Itraconazole systemically
- If severe or involves hair/nails
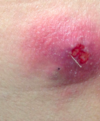
Soft tissue abscess
Describe Soft Tissue Abscesses?
- Within dermis or fat layers
- Walled-off infection and pooled pus
What is the treatment for soft tissue abscesses?
Surgical drainage

Cellulitis
Describe Cellulitis?
- Infection of dermis
- Begins in LLs then through lymphatics
- Caused by:
- S. aureus
- Beta-haemolytic streptococci
What is used to classify cellulitis?
Enron Classification
Describe the Enron Classification of Cellulitis?

Describe Streptococcal Toxic Shock?
- Toxin producing Group A Strep.
- Diffuse rash
- Primary infection in throat or skin
What is the treatment for Streptococcal Toxic Shock?
- Surgery to drain abscess
- Penicillin and Clindamycin
- Pooled human immunoglobulin in severe cases

Necrotising fasciitis
Describe Necrotising Fasciitis?
- Soft tissue infection with deep involvement
- Rapid, progressive damage
- Requires sugical debridement
What are the signs/symptoms of Necrotising Fasciitis?
- Rapid progression
- Pain out of proportion to clinical signs
- Severe systemic upset
- Visible necrotic tissue
Describe the use of imaging in Necrotising Fasciitis?
- May demonstrate fascial oedema and gas in soft tissues
- Late sign
What are the different types of necrotising fasciitis?
- Type 1 - Polymicrobial
- Type 2 - Group A Streptococcus
Describe type 1 Necrotising Fasciitis?
- Polymicrobial
- Usually complicates an existing wound
- Mix of gram positives, gram negatives and anaerobes









