Infections in the Immunocompromised Host COPY Flashcards
What is the Adaptive Immune Response split up in to?
- Humoral (B cells)
- Cellular (T cells)
What results if there is a compromised immune defence system?
Increased susceptibility to infection
What conventional pathogens may take advantage of a compromised defence system?
- Endogenous flora
- Hospital acquired bacteria
- Environmental organisms
Name some opportunistic pathogens which may take advantage of a compromised immune system?
- CoNS
- Aspergillus
What are the different types of immunodeficiency?
- Primary
- Secondary
Describe primary immunodeficiency?
- Inherited
- Exposure to i**n utero environmental factors
Describe secondary immunodeficiency?
- Underlying disease state
- Treatment for disease
What is the principal cause of morbidity and mortality in the immunocompromised host?
Infection
What is the most important risk factor for infection?
Neutropaenia
How is neutropenia defined?
Less than 0.5 x109/L
OR
Less than 1x109 and still falling
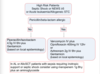
Draw a flowchart to show how neutropaenia can arise?

What happens to the incidence of infection neutropaenia duration?
The higher the duration of neutropaenia, the greater incidence of infection
What else is also important regarding neutrophils?
Neutrophil function
What can occur after a patient has received any of the following: cytotoxic drugs, irradiation and steroids?
- Reduced:
- Chemotaxis
- Phagocytic activity
- Intracellular killing
Describe Chronic Granulomatous Disease
- Inherited
- X-linked inheritance is most common
What is the cause of Chronic Granulomatous Disease?
- Defect in NADPH oxidase gene
- Oxygen radicals deficiency
- Normally give neutrophils their damaging effect
- Defective intracellular killing
How does Chronic Granulomatous Disease manifest?
- Abscesses
- Recurrent infections
- Granuloma formation
What is the pulmonary infection in Chronic Granulomatous Disease often caused by?
- S. aureus
- Aspergillus
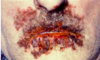
What does this child suffer from?

Chronic granulomatous disease
What is cellular immunity suppressed by?
- DiGeorge syndrome
- Malignant lymphoma
- Cytotoxic chemotherapy
- Extensive irradiation
- Immunosuppressive drugs
- Infections
Name some infections which can suppress immunity?
- HIV
- EBV
- CMV
- Mycobacterial
What do radiotherapy and chemotherapy ultimately cause?
Hypogammaglobulinaemia
What role does the spleen play in immunity?
- Splenic macrophages eliminate encapsulated bacteria
- Site of the primary immunoglobulin response
What is the site of the primary immunoglobulin response?
The spleen