Skin Flashcards
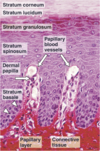
Epidermis
keratinized stratified squamous epith
Epidermis derived from ectoderm
Dermis
dense CT
Dermis derived from mesoderm
Hypodermis

subcutaneous tissue
not considered part of skin
Contains adipose
Epidermis Characteristics

Has deep invaginations- epidermal pegs
which interdigitate w/ dermis projections called dermal paipple
Thick & thin skin
Thick skin on palms of hands & soles of feet- no hairs
Thin skin has hairs & found everywhere else
Thickness depending on epidermis
Epidermis Breakdown
4 layers in thin skin
strat squamous

Keratinocytes
begin life @ bottom layer & as move up
cease dividing, diff, die & sloughed off (desqamation)
Stratum Basale
1 layer @ BM at dermal-epidermal junction
Contains stem cells w/ intense mitotic activity
As cells progress upwards, number of keratin intermed filaments increases until keratins represent half the total protein in stratum corneum
Stratum spinosum
Prickle cells- polyhedral keratinocytes; few layers
Desmosomes give them spiny or prickly appearance
Stratum Germanitivum
cells of lower stratum spinosum & stratum basale
only keratinocytes that divide!
Tonofilaments
another word for keratin intermed filaments in skin
Stratum granulosum
most superficial layer in which nuclei are still prsent
Cytoplasm w/ basophilic granules called keratohyalin granules!
Substance in keratohyalin granules binds w/ keratin filametns
Stratum granulosum & stratum spinosum

Both contain lamellar granules (lamellar bodies)
Lamellar granules- small rodlike structures formed by lipid bilayers
Discharge their content into IC space of stratum granulosum to be deposited as lipid sheets.
Barrier to penetration by foregin mat= sealing effect of skin
“waterproof” skin
LIKE INTERCELLULAR CEMENT
Stratum lucidum

clear layer just superficial to stratum granulosum
Can be observed only in palmar & plantar thick skin
Has keratinocytes w/o nukes or organelles just keratin filaments
stratum corneum
15-20 layers of dead cells
Non viable & scale like= squames
OUtermost layer is shed by desqamation
Much thinner in thin skin than thick skin
Changes of Keratinocytes
- mitotically active- statum bsale & lower spinosum
- nuke & organelles- up to stratum granulosum
- keratin/tonofilaments- get more as you move until top layer
- waterproof- granulosum & above
- desmosome- almost to top but not in stratum corneum
Thick skin
lines palms of hands & soles of feet
lack hair follicles
lack sebaceous glands
Thin Skin
Has epidermis
all over body
contains hair follicles & sebaceous glands
In thin skin

indiv cells of stratum granulosum & stratum lucidum are scattered at interface of stratum spinosum & stratum corneum.
Even though these 2 layers are absent or not well defined!
Callous
thickening of stratum corenum from P on A of skin
Most often in thick skin
Wart
benign epidermal growth due to papilomavirus infection of keratinocytes
Salicylic acid is Rx
- dissolves keratin (keratolytic)
Nonkeratinocytes in epidermis

melanocytes- syn dark brown pigment melanin
langerhan’s cells- APCs
Merkel cells- sensory mechanoR w/in nuero endocrine f
Melanocytes
Derived from NC cells
scattered among basal cells of stratum basale
Melanin begins to be degraded by lysosomes soon after it enters keratinocytes
Can replicate throughout their life, although much slower than keratinocytes

Melanocytes

syn melanin from tyrosine then transfer pigment into keratinocytes
Tryosinase syn in RER & accumulates in vesicles in Golgi & then as free vesicles= mealnosomes
Melanin syn begins in stage II melanosome & forms stage III melanosomes
Melanin granule is after stage III loses its tyrosinase activity
transferred to keratinocytes of malpighian layer (stratum basale & stratum spinosum) from melanocyte’s processes
Tyrosinase activated by UV light, this is why you tan when exposed to sun

















