Renal Histology Flashcards
Mar 7th 2013
Urinary System F
- Filters blood & produces urine
- eliminate metabolic waste & toxins from blood
- control H2O and ion balance by reabsorbing Na+ and secreting K+
- maintain acid-base pH of blood
- Regulate BP (produce & release renin)
Kidney Anatomy

Kidney Anatomy
From medullary pyramids’ base,
// arrays of tubules= medullary rays penetrate cortex
90-95% of blood pass through kidney in cortex
5-10% in medulla
Medulla has straight tubules & collecting ducts
Apex of pyramids= papillae which project into urinary parthway (minor calyces)
Nephron
individual f unit of kidney
filter blood & produces urine
Renal corpuscle found in cortex
& renal tubule

Nephron Anatomy
- Renal Corpuscle
- glomerular capillaries (glomerulus)
- Bowman’s capsule: contains filtrate, which is first step in urine forming
- Associated tubules
- continue w/ Bowman’s capsule, has many division w/ own type of cells
- tubule supposed to transform the filtrate into final urine
Renal Corpuscle
Blood enters through afferent arteriole, circulteas through tuft of capillaries & exits through efferent arteriole
The infiltrate enter urinary space & then proximal convoluted tubule
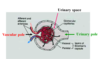
Glomerulus
Fenestrated endothelium
Covered by podocytes (visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule)
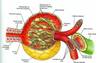
Common Basement Membrane of Podocytes

Podocyte
Visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule
Nuclei bulge out into urinary space
Common basal lamina b/t endothelium & podocytes
Cellular extensions further divide into pedicels.
Pedicels from 2 pdodocytes form filtration slits, which are spanned by thin mem
Have a phagocytic function!

Filtration barrier of glomerulus
Prevents passage of RBCs , leukocytes & platelets
Restricts proteins
Permits water, ions & other small molecs
Glomerulonephritis & diabetes- glomerular filter is altered & becomes more permeable to proteins (proteinuria)!

Cells w/in Corpuscle
Endothelium
Podocytes
Mesangial Cells
Mesangial cells
replace normal CT cells
Intraglomerular mesangial cells interspersed among capillary loops
Extraglomerular mesangial cells (lacis cells) in vascular pole
Contractile & phagocytic
Have R for Ang II & ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide in heart)
Cells of Corpuscle

Mesangial Cell Histo
Negative charges in BM

Tubules of Nephron- PCT
Infiltarte exits Bowman’s @ urinary pole & enter renal tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule- PCT, longest tubule in cortex
- Simple cuboidal, acidophilic, prominant long microvilli (brush border), basal striations
- reabsorb majority of ions- Na+, HCO3-, glucose, majority of H2O
- basal mem invaginations & associated mitochondria indicate= ion transporting f

Tubule of Nephron- Loop of Henle
Thick descending limb= simple low cuboidal, high osmotic P in CT, concentrates urine
Thick ascend limb= distal straight tubule, often termed part of first DCT, actively Na+ pump to CT
Thin Limb- simple squamous in medulla
Juxtamedullary nephrons= 1/7 of all nephrons
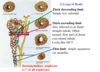
Tubule of Nephron- DCT
Last segment of nephron
simple cuboidal, few microvilil
When cut in cross section, has more nuclei than PCT
site of mech that controls total salt & H2O content of body: if enough aldosterone is present, Na+ is absorbed & K+ is secreted out of the body.
PCT vs. DCT
PCT- more acidpholic, brush border
DCT- more nuclei, no brush border, larger lumen

Juxtaglomerular apparatus
up reg BP
Macula densa- specialized DCT portion, sense Na+ [] in infiltarte
Juxtaglomerular cells- modified smooth m. in walls of afferent arteriole, sense BP & produce renin
Lacis cells- mesangial cells, may contain some granules & contiguous w/ intraglomerula mesangial cells
Cell Histo

Tubules of Nephron- Collecting tubule/ducts
Urine passes from DCT to collecting tubule
Collecting tubule merge in medullary ray to form cortical collection ducts
Cortical collecting ducts continue into pyramids where merge to form large ducts
Duct of Bellinie- large collecting duct, open @ papillae into minor calyx
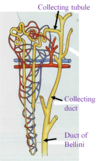
Collecting tubule & duct
Have dark cells (intercalated cells) - secrete H+
& light cells (principal cells)- respond to ADH
Medullary Collecting duct- mainly principal cells, distinct lateral margins, few microvilli & clear cytoplasm

Blood supply in nephron

Excretory passages
Calyces, ureter, urinary bladder & upper part of urethra
- calyces:
mucosa- transitional epith, lamina propria
muscularis
adventitia






