Female Reproductive Sys Flashcards
Hormonal Control
pulsatile release of GnRH to start puberty
All follicles in ovarian cortex prior to that are primordial follicles
Relase of LH & FSH from basophils of ant pituitary
Hormonal Control

Ovary

Cortex- various ovarian follicle stages, corpus luteum & corpus albicans
Medulla- loose CT, BV, lymphatic vessels, n. fibers
Germinal epithelium- modified peritoneum, covers ovary from mesothelium & composed of simple cuboidal cells
Tunica albuginea- dense CT beneath germinal epithelium
Ovarian Cortex

Stroma w/ stromal cells & ovarian follicles
Primordial germ cells (oogonia) are from yolk sac endoderm & migrate to developing goand in 6th week.
Undergo mitosis until near end of 5th month- 5 to 7 mill oogonia
Only 1 mill oogonia will be surrounded by follicular cells & survive to time of birth.
Remaining oogonia atrophy
Cycle continued

Oogonia that survive enter prophase I & known as primary oocyte
Meiosis is arrested in diplotene stage of meiosis I by OMI produced by follicular cells.
Total of 450 ooocytes released over the entire reproductive years
All other follicles degen & die.
Different Stages of Follicle/Oocyte

FSH Indep
Primordial Follicles (non growing)
Primary/prenatral follicles (growing)
FSH dep
Secondary/antral follicles (growing)
Mature or Graafian follicles (preovulatory) (growing)
Ea follicle contains primary oocyte surrounded by 1 or multilayer follicular or granulosa cells
Secondary oocyte formed before ovulation when the oocyte completes first meiotic division
Primordial Follicle

Smallest & most numerous type of follicles in cortex of ovary.
Ea is composed of 1 layer of flat follicular cells around primary oocyte separated from stroma by basement mem
Primary oocyte arrested in prophase I - 1 nucleus, Golgi, RER, mitoch, lysosomes
Primary Follicles

Oocyte grows
- unilaminar primary follicle- primary surrounded by simple cuboidal or columnar follicular cells single layer
- multilaminar primary follicle- follicular cells prolif & stratify, & now are granulosa cells. Prolif of follicular cells is due to activin produced by primary oocyte
Multilaminar Primary Follicle

Zona Pellucida
during primary follicle stage, an amorphous substance appears, separating oocyte from follicular cells.
Contains ZP1, 2, 3 secreted by oocyte & form extracell coat of glycoprotein
ZP-3 is most important, acts as R for sperm binding & for inducing acrosomal rxn
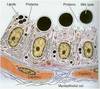
Theca interna, theca externa, granulosa cells
Stromal cells around multilaminar primary follicle (theca folliculi) form inner theca interna (richly vascular layer) & outer theca externa (fibrous CT)
Theca interna cells: steroid producing cells, possess LH R on cell mem & influenced by LH.
Produce androstenedione (male sex hormone), which enters granulosa cells where converted to estradiol by aromatase.
Granulosa cells & theca interna are seprated by thickened basal lamina
Secondary/Antral Follicles

Characterized by accumulations of fluid known as liquor folliculi among granulosa cells
Prolif of granulosa cells depends on FSH, & possess FSH R.
FSH & estrogen induce granulosa cells to express LH R
Primary oocyte bigger but no further growth due to OMI!
Liquor folliculi- exudate of plasma, w/ GAGs, proteoglycans, steroid binding proteins & hormone (estradiol, inhibin, activin)
Follicle

most of follicles reach this stage undergo atresia
Some granulosa cells associate w/ atretic follicles form interstitial glands which secrete estrogen until menopause
Few secondary follicles continue to develop into mature follicles

Light pink= collapsed ZP
Dark pink= BV
Mature Graafian Follicle

Droplets of liquor folliculi coalesce to form single fluid filled chamber called antrum.
Granulosa cells rearrange & primary oocyte is surrounded by small group of granulosa cells called cumulus oophorus
Single layer of granulosa cells that immediately surrounds primary oocyte is called corona radiata
Cell structure
continued formation of liquor folliculi causes cumulus oophorus composed of primary oocyte, corona radiata & associated follicular cells to detach from its base & float freely w/in liquor folliculi.
Secondary oocyte is fomred shortly before ovulation when oocyte completes first meiotic division
Corpus Luteum
Formed from Graafian follicle that ovulated
Clot removed by phagocytes, high LH levels change structure
F as temporary endocrine gland & supports uterine endometirum

Cell Model
Progesterone always exert - feedback
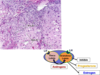
Lutein Cells
Granulosa lutein- 80% of corpus luteum, pale staining steroid producing cells, produce mainly progesterone & estrogen
Theca lutein- 20% corups luteum, dark staining, secrete androgens & minor progestrone amts
Fate of Corpus Luteum
If pregnancy occurs- hCG from placenta maintains corpus luteum for 3 months.
Now its corpus luteum of pregancne & secreted hormones.
Intro of PG could cause degen of corpus luteum & abortion of fetus.
Placenta eventually takes over progesterone production & corpus luteum degrades into corpus albicans w/o fetus loss
If no pregnancy- corpus luteum stops secreting progesterone & decays. Degen to corpus albicans.
Atretic Follicles
Follicles that undergo degeneration
Of all follicles present in ovaries @ menarche, only 0.1-0.2% develop to maturity & undergo ovulation.
Ovarian medulla
richly vascular fibroelastic CT
Hilar cells (like Leydig, secrete androgens)