Renal Embryology Flashcards
Three Kidney Systems
Derived from intermed mesoderm
Pronephros
Only appear in week 4
Cervical & upper thoraci region
Segmented
Form vesitigial excretory units- nephrotomes
Regress by end of 4th week- non f
mesonephros
Unsegmented mesonephros- nephrogenic cord
mesonephric (wolffin) ducts- from upper thoracic to upper lumbar L3 segments
Early in 4th week
Excretory tubules derived from unsegmented mesonephros
Week 7- baby produces urine, cloacal mem ruptures, pee comes out of membrane into amniotic cavity, baby swallows its own pee with amniotic fluid
By 2nd month- mesonephros & mesnephric ducts disappear
In males, part of caudal tubules & mesonephric ducts remain & participate as vas deferns (part of it)

Metanephros
Definitive kidney
Appears in week 5, nephros develop from metanephric mesoderm
Permanent Kidney
2 origins:
metanephros- 3rd kidney sys, excretory unit (Bowman’s capusle, PCT, loop of Henle, DCT)
mesoneprhos- uteric bud, collecting sys (collecting tubule, duct, minor & major calyces, renal pelvis, ureter)
Uteric Bud
Outgrwoth of mesnephric duct
Primordium of collecting sys (collecting tubule–> ureter)
Early 5th week
3rd kidney system!
Collecting Sys
From ureter to collecting tubules
Mesonephric origin (ureteric bud)

Bowman’s capsule to DCT
Metanephric origin:
- ureteric buds continue to bifurcate until 32nd week, produce 1-3 million collecting tubules
- tip of ea collecting tubule induces dev of metanephric tissues cap, continues to lengthen to form Bowman’s capusle to DCT
- metanephric tissue= surrounds collecting tubule & duct

Final Kidney
Definitive kidney created b/t 5-15 week
Urine produced by kidnye passed into amniotic cavity in 12th week
During fetal life, kidneys NOT RESPONSIBLE for waste excretion.
Reciprocal induction b/t metanephric mesenchyme & ureteric bud
WT1; expressed by mesenchye, TF that makes this tissue competent to respond to induction by ureteric bud
no WT1= no kidney
Wilm’s Tumor/ nephroblastoma
WT1 mutation, rapidly form malignancy
<5 yo
WAGR Syndrome
Wilm’s tumor
Aniridia (no iris in eye)
Genitourinary anomalies
Mental retardation
Hemihyperthrophy
Chome 11 deletion
Obesity
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney
Nephrones fails to dev, collecting duct never forms
1/2400
Renal Agenesis
No kidney
Ureteric bud fails to contact & induce metanephric mesenchyme
U/L: 1/1000, usually male, asymptomatic
B/L: char facial appearance & oligohydramnios
Potter Seq
typical appearance of fetus or neonate due to oligohydramnios in utero
Lack of kidney, anuria, oligohydramnios (low volume of amniotic fluid), hypoplastic lungs; other abnormalities (under dev lungs, club foot etc. )
Congenital Polycystic Kidney CPK
Numerous cysts formed in kidney, autosomal trait
Auto recessive PK= progressive, cysts form from collecting ducts, infancy or childhood renal failure
Autosomal dominant CPK= less progressive, cysts form from all segments of nephron, adult renal failure
Duplication of Ureter
Early splitting of ureteric buds

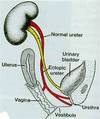
Ectopic ureter
Dev of 2 ureteric buds
One normal & other moves down with mesonephric duct
Entrance in bladderm urethra, vagina
Embryonic Origin
A= PCT; 3rd kidney sys (metonephros)
B= thin limb, 3rd (metonephros)
D= collecting duct, 2nd (ureteric bud(

Kidney Position
Ascend from their original region (sacral) to lumbar site.
Definitive position is attained by 9th week

Abnormal Kidney Location
Pelvic kidney- asymptomatic
Horeshoe kidney- ascent of kidneys prevetned by IMA, asymptomatic but Wilm’s tumor occurs more frequently

Bladder & Urethra
From cloaca
During 4-7th week, cloaca divided by urorectal septum into rectoanal canal (post)
primitive urogenital sinus (und)
Bladder
Prostatic & membranous urethra
Definitive urogenital sinus- vestibule of vagina or penile urethra

Bladder Formation
Majority of bladder- primitive urogenital sinus (endoderm)
Trigone- mesonephros (intermed mesoderm)

End 3rd Month
Outgrowth from urethra:
male- prostate gland
female- urethral glands & paraurethral glands
Budding from ductus deferens- seminal vesicles





