Skeletal System Flashcards
what is the skeleton composed of?
- Bone
- Cartilage
What are the 2 types of bone?
- Compact
- Spongy
What are the features of bone?
- Matrix is solid
- 35-45% water and organic matter
- 55-65% crystallized minerals (calcium/phosphate)
- Vascular
- Innervated
what are the 3 types of cartilage in skeletal system?
- hyaline
- elastic
- fibro
what are the features of cartilage?
- matrix is flexible
- 75% water
- collagen/elastin fibres in gel like substance
- gel like substance = chondroitin sulphate
- avascular
- no nerves
what is connective tissue?
cells and fibres immersed in a ground substance (matrix)
what are the 4 cell types in bone?
1) ostogenic cells
2) osteoblasts
3) osteocytes
4) osteoclasts

what are ostogenic cells?
undifferentiated cells
- other cells arise from this cell (become osteoblasts)

what are osteoblasts?
forms the matrix and collagen fibres but can’t divide
- makes the matrix to make our bones
- osteoblasts turn into osteocytes

what are osteocytes?
mature cells that no longer make up the matrix
- do not divide/ secrete matrix

what are osteoclasts?
huge cells that function in bone resorption
- breaks down bone matrix
- does not originate from ostogenetic cell

where is compact bone located?
shaft of long bones and external layer of all bones
what are some compact bone facts?
- organized and strong
- contains yellow bone marrow that stores triglycerides (fats)
what is the structure of compact bone?
- osteon/haversian system
- haversian canal
- lacuna/lacunae
- concentric rings/ lamellae
- canaliculi
- osteocytes
what is the osteon/haversian system?
concentric rings of calcified matrix surrounding haversian canal

what is lamellae?
the concentric rings surrounding the osteon/haversian system
what are lacunae?
empty spaces in osteon containing osteocytes
where are osteocytes found in compact bone?
lacuna
what is canaliculi?
small canals that connects one cell to another to let in nutrients/oxygen to cells in lacuna
- how osteocytes communicate
what is canaliculi filled with?
extracellular fluid
what is the haversian canal?
canal in centre of osteon/haversian system that blood vessels, lymph vessles, and nerves run through
where is spongy bone located?
end of long bones and inside flat bones
what does spongy bone look like?
- less organized
- comprised of trabeculae and space for red bone marrow

what is trabeculae?
thin plates of bone in a fence like structure positioned along lines of stress

what are the spaces in the trabeculae filled with and why?
red bone marrow
- formation of red and white blood cells
what are the 6 functions of bone?
1) protection
2) support
3) movement
4) forms units
5) blood cell production
6) storage
cartilage facts
- no blood vessels or nerves
- composed of chondrocytes (mature cartilage cells)
- occurs in lacunae
- matrix contains translucent proteins
what makes up the matrix in catrilage?
chondroblasts
why does cartilage stay thin?
due to being avascular
what is perichondrium and what is the function?
connective tissue surrounding cartilage
- function: blood vessels diffuse nutrients into cartilage
what are the 5 functions of cartilage in skeletal system?
1) forms embryonic skeleton (before born)
2) protection
3) cushioning
4) joins some bones
5) support/flexibility
what are the 5 major types of bone?
1) long bone
2) short bone
3) irregular bone
4) sesamoid bone
5) flat bone
what determines a long bone/example?
longer in length than width
ex: femur, radius
what determines a short bone/example?
approx equal length and width
ex: tarsals, carpal
what determines flat bones/example
flat/thin and greater area for muscle attachment
ex: scapula, ribs
what determines irregular bones/examples
can’t assign a shape to it
ex: some facial bones
what determines sesamoid bones/examples
bones within ligaments/tendons
ex: patella
often classified as irregular
what are the 2 principle components of a skeleton?
1) axial
2) appendicular
how many bones are in the body and how many bones do the axial/appendicular components contain?
206 bones total
80-axial skeleton
126- appendicular skeleton
what are the principle components of the axial skeleton?
- skull
- hyoid bone
- vertebrae
- ribs
- sternum
- ear ossicles
**the skull, vertebrae and rib cage**
what are the bones in the skull?
1) parietal bone
2) frontal bone
3) occipital bone
4) temporal bone
5) maxilla
6) mandible
what bone is located in the anterior neck?
hyoid bone

what 3 bones are included in the skull?
1) malleus
2) incus
3) stapes
what is the thorax?
a cage of bones
where are the 2 locations that ribs are attached?
1) vertebral column at the back
2) sternum in front using hyaline cartilage
how many ribs do we have ?
12
what are ribs 1-7 called and location?
true ribs
- attached by hyaline cartilage at sternum
what are ribs 8-10 called and location?
false ribs
attached together by hyaline cartilage that is attached to 7th rib
what are ribs 11 + 12 called and location?
floating ribs
not attached to sternum
how many bones consists of the vertebral column and what are the different vertebrae names?
26 bones
1) cervical vertebrae (7) - neck
2) thoracic vertebrae (12) - chest
3) lumbar vertebrae (5) - lower back
4) sacrum (1 from 5 fused vertebra) - pelvis attaches
5) coccyx (1 form 4-5 fused bones)

what are the functions of the vertebral column?
- strong/flexible
- protects spinal cord
- supports the skull
- provides attachments of ribs and muscles
what sections of the vertebral column is concave/convex?
concave:
- cervicle
- lumbar
- coccyx
convex:
- thoracic
- saccral
what does a typical vertebrae consist of?
- centrum (vertebral body)
- vertebral foramen
- transverse process
- spinous process

what is the vertebral foramen?
opening that contains spinal cord
what is the first cervical vertebrae and why?
atlas
- holds skull
what is the difference of atlas and axis complex?
Atlas:
- supports the head
- has no centrum (body)
- 2 large superior surfaces which allows nodding movements
Axis:
- centrum is peg shaped (dens)
- atlas swivels around axis & dens (side to side movement)
- longer spinous process than atlas
what are the components and functions of the pectoral girdle?
- clavicle (anteriorly)
- scapula (posteriorly)
- hold upper limbs to axial skeleton
what are the components and functions of the pelvic girdle?
- ilium
- ischium
- pubis
**fused together = innominate bone**
- supports axial skeleton and allows some flexibility to pelvis
what makes up the upper limb?
1) clavicle
2) scapula
3) humerus
4) radius (same side as thumb)
5) ulna
6) carpals
7) metacarpals
8) phalanges
what makes up the lower limb?
1) hip bone (innominate bone)
2) sacrum
3) femur
4) patella
5) tibia
6) fibula
7) tarsals
8) metatarsals
9) phalanges
what is the enlarged tarsal that forms the heel?
calcaneus
what is the difference of a male and female skull?
Male:
- bones generally larger/heavier
- skulls generally larger
- larger jaw/teeth
- forehead tends to slope more
Female:
- bones smaller/lighter
- skull generally smaller
- smaller jaw/teeth
- forhead does not slope as much
what is the most common and effective way to distinguish between a male and female skeleton?
examination of the pelvis
what is the difference of a male and female pelvis?
Male:
- heavier
- more narrow
- opening is smaller/more pear shape
- funnel shaped pelvis
Female:
- broader, lighter, smoother
- opening is larger/ more circular for childbirth
- basin shaped pelvis

what is the difference of pubic arch angle for male and female?
Male: smaller than 90 degrees
Female: Greater than 90 degrees

what is the difference of curvature in sacrum ad coccyx for male and female?
Male: more anterior curvature
Female: less anteior curvature

what is the difference of the skull for babies vs adults?
Baby: length of skull is 1/4 of body length
Adult: length of skull is 1/8 of body length
what is the difference of ossification in babies vs adults?
babies:
- less ossification
- fontanels in baby skull
- more cartilage than bone
Adults:
- Fontanels have fused together
what are fontanels?
cartilage between bones in baby skull
what is the difference of curves in vertabral column for babies vs adults?
Babies: single curve in fetus
(due to being in that position for 9 months)
Adults: 4 curves
what is the head of the bone called?
proximal/distal epiphysis

what is the neck of the long bone called?
Metaphysis

what is the shaft of the long bone called?
diaphysis

what is the epiphysial line?
region where bone grew in length
** after bone stops growing**
- 2 in long bone
- in metaphysis
what is the epiphysial plate?
region where bone has room to grow
what is the medullary cavity in long bone?
cavity in shaft of bone that contains blood vessels and is a storage area for fat
what is endosteum?
thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity that contain cells involved in bone formation/maintenance
what is perioteum?
tough membrane that covers the outer surface of the bone
- contains cells involved in bone formation/maintenance
- contains blood vessels which aids in bone nourishment
what are the 2 types of ossification?
1) intramembraneous ossification
2) endochondral ossification
what is ossification?
bone formation
what is the difference of intramembraneous ossification and endochondral ossification?
intramembraneous- forms flat bones
endrochondrial- forms majority of bones
what are the steps of intramembranous ossification?
1) mensenchymal cells come together to becomes osteoblasts
2) osteoblast start secreting uncalcified matrix
3) osteoblast becomes calcified, differentiating into osteocytes
4) matrix then forms around blood vessels forming trabeculae (spongy bone)
5) the osteocytes at the end of spongy bone rearrange into osteon which surrounds spongy bone
6) periosieum is then developed
what are the steps of endochondral ossification?
1) starts with hyaline cartilage w/ mesenchymal cells present
2) mesenchymal cells in hyaline cartilage becomes chondrocytes
3) chondrocytes then secretes cartilage matrix
4) chondrocytes starts to die when matrix is calcified
5) blood vessles then invade the cartilage which makes osteoblasts secrete bone matrix
6) spongy bone starts to replace cartilage and spreads to ends of bones
7) osteoclasts starts ti breakdown some inside of spongy bone, producing the medullary cavity. Spongy bone at shaft is replace dby compact bone
8) more clusters of osteoblasts are differentiated at the end of bones
9) the remaining hyaline cartilage surrounding secondary ossification centre becomes articular cartilage/ epiphyseal plate
what does the ackrynom Bones Can’t Pop During Exercise stand for?
B- bone collar formation
C- cavitation
P- Periosteal bud invasion
D- Diaphysis elongation
E- epiphyseal ossification
what are 3 factors affecting ossification?
1) heredity (genetics)
2) nutrition
3) hormones
how does bone grow in length?
growth at the epiphyseal plate

what are the 4 zones of the epiphyseal plate?
1) zone of resting cartilage
2) zone of proliferating cartilage
3) zone of hypertrophic cartilage
4) zone of calcified cartilage
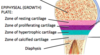
what is the function of zone of resting cartilage?
no bone growth, anchor cartilage to bone
what is the function of zone of proliferating cartilage?
chondrocytes are dividing and secreting extracellular matrix
**in growing carrtilage, chondrocytes can divide**
what is the function of zone of hypertrophic cartilage?
mature chondrocytes
cells enlarge and then die
what is the function of zone of calcified cartilage?
- dead chondrocytes that have been calcified
- osteoclasts deissilve cartilage
- osteoblasts starts to lay down new bone replacing the cartilage
how does long bone grow in girth for events in periosteum?
- periosteum cells differentiate into osteoblasts
- osteoblasts lay down new compact bone around periosteal blood vessels
- osteoblasts differenciate into osteocytes
how does long bone grow in girth for events in the endosteum?
- osteoclasts erode endosteum
- calcium is released into the blood stream
- medually cavity enlarges (increases bone size w/o increasing bone weight)
what are the 4 types of bone fractures?
1) simple (closed) fracture
2) compoud (open) fracture
3) comminuted fracture
4) greenstick fracture
what is simple (closed) fracture?
clean break and bone does not protrude through skin
what is compound (open) fracture?
clean break, skin protrudes out of skin
what is comminuted fracture?
bone is crushed/ splintered at the break and fragments lie in between
- happens mainly with elders
what is greenstick fracture?
only one side of the bone is broken, other side is bent
- often happens with small children


