Signal Transduction Flashcards
(34 cards)
Specificity
Signal molecule fits binding site on its complementary receptor; other signals do not fit.

Ampification
When enzymes activate enzymes, the number of affected molecules increases geometrically in an enzyme cascade.

Modularity
Proteins with multivalent affinities form diverse signaling complexes from interchangeable parts. Phosphorylation provides reversible points of interaction.

Desensitization/Adaptation
Receptor activation triggers a feedback circuit that shuts off the receptor or removes it from the cell surface.

Integration
When two signals have opposite effects on a metabolic characteristic such as concentration of a second messenger X, or the membrane potential Vm, the regulatory outcome results from the integrated input from both receptors.

G protein-coupled receptor
External ligand binding to receptor activates an intracellular GTP-binding protein, which regulates an enzyme that generates an intracellular second messenger.
Receptor tyrosine kinase
Ligand binding activates tyrosine kinase activity by autophosphorylation.
Receptor guanylyl cyclase
Ligand bindind to extracellular domain stimulates formation of second-messenger cyclic GMP.
Nuclear receptor
Hormone binding allows the receptor to regulate the expression of specific genes.
General features common to all signal transduction

G protein coupled receptor and second messenger
Transduction of epinephrine signal: the B adrenergic pathway

Actions of adenylyl cyclase and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase

Self-inactivation of Gs

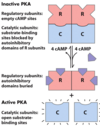
Activation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA)
Amplification of epinephrine signal cascade

Disruption of G-protein signaling causes disease

Role of hormone activated phospolipase C Diacylglycerol, IP3, and Ca2+ as second messengers
Cellular action affected by these types of signal includes: neuronal & immune functions and regulation of cell growth.

Two second messengers are derived from phosphatidylinositol
Diacylglycerol and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3)
_______ acts as a second messenger in signal transductions.
Calmodulin
Regulation of gene expression of insulin
“Receptor Tyrosine Kinase”
Insulin receptor is tyrosine specific protein kinase

Regulation of glycogen synthase or glycogen biosynthesis

Mechanism of activation of Glycogen Synthase by insulin

Receptor Guanylyl Cyclases, cGMP and Protein Kinase G
Receptor Guanylyl Cyclases generate the second messenger cyclic-GMP (cGMP)

Two types of Guanylyl Cyclase that participate in signal transduction











