session 4 Flashcards
(28 cards)
what are the layers of the cerebellar cortex?
molecular
puurkinje
granular
what are the input fibres for the cerebellum? & where do they input?
Mossy fibres - middle cerebellar peduncle
climbing fibres - inferior cerebellar peduncle
what information is inputted through the middle peduncle?
corticopontocerebellar tract - primary motor cortex = motor planning
what information is inputted through the inferior peduncle?
- muscle proprioception from the dorsal spinocerebellar tract
- vestibular balance information from the vestibular cerebellar tract
what is the output of the cerebellum? where does it leave? where does it go?
- purkinje cell axons
- leaves through the superior peduncle
- goes to mid brain, diencephalon and cerebrum
describe the communication of mossy fibers in the cerebellar cortex?
- synapse with granular cells in granular layer
- granular cells project axons to the molecular layer
- become parallel fibrers and synapse with purkinje cells
- many parallel fibres to one purkinje cell
describe the communication of climbing fibers in the cerebellar cortex?
- synapses to purkinje cells
- 1-1 synapse
what fibers are excitatory? what are inhibitory?
excitatory = climbing, mossy and granular
inhibitory = purkinje
describe the communication of climbing fibers in the cerebellar cortex?
-synapses to purkinje cells -1-1 synapse
what fibers are excitatory? what are inhibitory?
excitatory = climbing, mossy and granular inhibitory = purkinje
What is comunicated through the superior cerebellar peduncle? where does it go to?
ventral spinocerebellar tracts - sensory input for balance and proprioception (contralateral)
spinocerebellum/paleocerebellum = vermis + paravermal regions
+
efferent purkinje cells from the dentate gyrus to pontine nuclei/thalamus/cortex
what does the floculonodular lobe do?
it is the archiocortex of the cerebellum and regulates balance and head eye coordination
Where does the flocoulonodular lobe recieve inputs from?
vestibulo inputs from the vestibulocochlear nerve and from CN 2 from the superior colliculus
What does the spino cerebellum (vermis and paravermis region) do?
- it’s concerned with axial control and gait
- outputs via the fastigial and interposed nucleus to the medial and lateral descending pathways.
What does the cerebrocerebellum (lateral cerebellar hemispheres) do?
concerned with motor planning - has outputs to the thalamus, motor and premotor corticies via DENTATE
What is this nucleus and what does it do?

This is the dentate nucleus - largest and only visbile nucleus in a living specimen
-planning, intiation and control of movement
What is the fissure called that separtes the anterior and posterior lobes?
Primary fissure
Where do the denate nucleus fibres leave the cerebellum?
superior cerebellar peduncle
what are the cerebellar deep nuclie in order from medial to lateral?
fastigule, interpose and denate
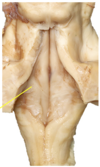
what is the yellow line point at?

Facial colliculus
What is the yellow line pointing at?

hypoglossol trigone
What is the yellow line pointing at?

median sulcus
what is the yellow line pointing at? what does it signify?

Medullary striae - pontocerebellar fibres that devide the floor fo the 4th ventricle into pontine and medullary
what is the yellow line pointing at?

The obex - rostolaterally near it is the area postrema the chemoreceptive emetic centre