Scapular and Pectoral Regions Flashcards
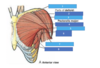
Red
Black
Green

- Red- Scapula
- Green- Clavicle
- Black- Manubrium
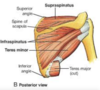
Yellow
Blue
Red

Yellow Humerus
Blue Radius
Red Ulna
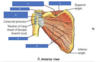
Purple
red
yellow
blue
orange
pink
black
brown
Green

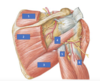
Purple:Scaphoid(boat looking),
Red:lunate(half moon),
yellow: triquetrum,
Blue: pisiform (shaped like a pea),
Orange: trapezium (trapezithumb),
Pink: trapezoid,
Black: capitate,
Brown: hamate(oink)
Green: Metacarpals
Red”
yellow
purple

Red: prox. phalanges
Yellow middle phalanges
Purple distal phalanges
What Bones make up the Pectoral Girdle?
Scapula
Clavicle
Manubrium
What bone makes up the arm (aka the _____)?
Aka brachium
Humerus
What bones make up the forearm (aka the_____)?
What are these bones bound together by?
Aka the (antebrachium)
Radius
Ulna
Bound together via interosseous membrane
What Bones does the wrist (aka ____) consist of?
Carpus
8 bones: Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
Of the five metacarpals, which one is lateral and which is medial? How do you number?
Lateral- goes to thumb and is #1
medial- pinky side is #5
The thumb is digit #__ and has ___ phalanges called what?
The pinky is digit #__ and has ___ phalanges called what?
How many phalanges do the rest of the digits have? called?
5, with three phalanges, distal, middle, proximal
Thumb-
#1, with 2 phalanges one distal and proximal
Pinky:
Digits #3-5
all have three phalangse with distal, middle and proximal halanges
____ ____ snugly encloses the muscles of the upper limb and is continuous over the_______, _____, and ___ ___.
Deep fascia
pectoral girdle, axilla and upper limb.
Lable 1-9

- deltoid fascia
- pectoral fascia
- brachial fascia
- antebrachial fascia
- palmar carpal ligament
- superficial transverse metacarpal ligament
- bicipital aponeurosis
- tendon of palmaris longus
- palmar aponeurosis

what are the regional designations of fascia in the upper limb? (5)
Axillary fascia
Brachial fascia
Antebrachial fascia
Palmar fascia
Digital fibrous sheaths
Brachial fascia extends ____ to attach to the ____ as ___&____ _____ ____ that compartmentalize muscles of the ____
deep
humerus
medial&lateral intermuscular septae
arm
What is this a cross section of?
Label 1-5

the arm
- lateral intermuscular septum
- Brachial fascia
- medial intermuscular septum
- skin
- shaft of humerus
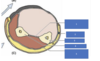
Antebrachial fascia is thickened at the ____, _____ &_____ as the ____ & _____ ____, respectively
wrist
anteriorly
posteriorly
flexor and extensor retinaculum
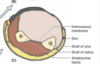
This is a cross section of the what?
Label 1-5.
forearm
- interosseous membrane
- skin
- shaft of the ulna
- shaft of the radius
- antebrachial fascia

This is a cross section of the?
label 1-8
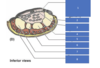
Wrist
- flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament)
- hamate
- palmar carpal ligament
- carpal tunnel
- capitate
- trapezoid
- trapezium
- extensor retinaculum

There are two patterns of sensory innervation that occur in the upper limb: First, there is _____ ___ (____) that is done by the ____ ____. Next, there is ____ ____ done by _____ ____ from the _____ ___.
segmental innervation (dermatomes) by spinal nerves
multisegmental innervation by peripheral nerves from the brachial plexus
The____ ____ is the main source of arterial blood for the upper limb. It gives rise to several branches, including the ____ __, which supplies muscles of the scapula via _____ and ____ _____ arteries.
subclavian artery
thyrocervical trunk
suprascapular and transverse cervical
The subclavian artery becomes the ____ ___ as it crosses the ____ border of the first rib. It gives rise to multiple branches that will be discussed with the axilla.
axillary artery
lateral border
When it crosses the lower border of ___ ____, the axillary artery becomes the ____ ____ that travels through and supplies structures in the arm. It gives rise to the deep ____ _____ (_____ ____), as well as the superior and inferior ____ ____ ____.
teres major
brachial artery
brachial artery (profunda brachii)
ulnar collateral arteries.
The brachial artery splits into the ___ &____ ____anterior to the elbow.
radial and ulnar arteries
The ulnar artery gives rise to several branches in the forearm, including: ____ ____ ___ and the ____ ____ ____which splits into anterior and posterior____ ____). The ulnar artery terminates as the ___ ____ ____ in the hand.
ulnar recurrent artery and
the common interosseous artery
interosseous arteries
superficial palmar arch
The _____ ____ travels along the lateral forearm, giving rise to the ___ ____ ___ and terminating as the ____ ___ ____in the hand.
radial arteryradial recurrent artery
deep palmar arch in the hand.
what are the two types of veins in the upper limb?
deep and superficial
Deep veins lie inside the deep fascia and occur as ___ ___ or accompanying veins that travel with and are named for the ___ ___ of the upper limb.
“venae comitantes,
major arteries