S7) Neuronal Control of Micturition Flashcards
What is micturition?
Micturition is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body (urination)
In 5 steps, describe the basic process of micturition
⇒ Urine is made in the kidney
⇒ Urine is stored in the bladder
⇒ Sphincter muscles relax
⇒ Detrusor muscle contracts
⇒ Bladder is emptied through urethra & urine is excreted
Identify 5 functions of the nervous system in relation to the lower urinary tract
- Provides sensations of bladder (distension & pain)
- Relaxes bladder
- Accommodates increasing volume of urine
- Initiates & maintains voiding
- Regulates of smooth & skeletal muscle sphincters
Briefly, describe the structure and location of the bladder
- Location: situated anteriorly in the pelvic cavity
- Structure: hollow, highly distensible, rounded in shape

State 2 functions of the bladder
- Temporary storage of urine (~600ml)
- Assists in the expulsion of urine
The morphological appearance of the bladder varies with filling.
Illustrate this
- When full, it exhibits an oval shape
- When empty, it is flattened by the overlying intestines

The bladder has 3 major functional muscular units that play a critical role in normal functions.
Identify these 3 regions
- Apex
- Neck
- Body

Describe the entry and exit of urine in relation to the bladder
- Urine enters the bladder by the left and right ureters
- Urine exits via the urethra

The internal urethral orifices are marked by the trigone.
What is this?
- The trigone is a triangular area located within the fundus
- In contrast to the rest of the internal bladder, it has smooth walls

There are two sphincters controlling the outflow of urine.
Identify them

Distinguish between the structure of the male and female IUS
- Male IUS consists of circular smooth fibres, which are under autonomic control
- Female IUS has no sphincteric muscle present and is formed by the anatomy of the bladder neck and proximal urethra
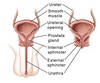
The external urethral sphincter has the same structure in both sexes, hence, describe its structure and function
- Structure: skeletal muscle, and under voluntary control
- Function: relaxes during micturition to allow urine flow

Describe the structure and function of the detrusor muscle in the bladder wall

- Structure: specialised smooth muscle, with fibres are orientated in three directions to retain structural integrity when stretched
- Function: allows bladder contract during micturition
Which divisions of the nervous system innervate the detrusor muscle during micturition?
- Parasympathetic nervous system
- Sympathetic nervous system
Where along the extent of the urinary system is the following image from?

Trigone – only location in the bladder where the detrusor muscle consists of three layers
Name the structres M, S, LP shown in the photomicrograph below

M – mucosa
S – submucosa
LP – lamina propria
Which muscle composes layers 1,2,3 shown in the photomicrograph below?

Detrusor muscle – fibres oriented in 3 different directions in area of trigone
Identify which divisions of the nervous system provide innervation to the bladder
- Somatic nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system (parasympathetic & sympathetic)
The sympathetic innervation of the bladder promotes urine retention (continence).
Describe the structures involved
SNS communicates with the bladder via the hypogastric nerve (T12 – L2), causing the relaxation of the detrusor muscle
The parasympathetic innervation of the bladder stimulates voiding (micturition).
Describe the structures involved
PNS communicates with the bladder via the pelvic nerve (S2-S4), causing the contraction of the detrusor muscle
Somatic nervous system provides voluntary control over micturition.
Describe the structures involved
Somatic innervates the external urethral sphincter via the pudendal nerve (S2-S4) to constrict (storage phase) or relax (voiding phase) it
Where are the sensory (afferent) nerves located and what do they do?
Afferent fibres of the pelvic nerve are found in the bladder wall and convey sensory information (distension & pain) to the brain
In 3 steps, describe the neuronal control over the storage/continence phase of micturition

Which brain centre is responsible for the storage of urine?
Pontine storage centre
Which sympathetic receptors are involved in the storage phase?
- α1 receptors at the IUS (contracts sphincter)
- β3 receptors at the detrusor muscle (relaxes bladder)
What is the postganglionic neurotransmitter for the sympathetic receptors in the storage phase?
Noradrenaline
In 5 steps, describe the neuronal control over the voiding phase of micturition

Which brain centre is responsible for micturition?
Pontine micturition centre
Which parasympathetic receptor is involved in the voiding phase?
M3 receptors at the detrusor muscle (excited)
What is the postganglionic neurotransmitter for the parasympathetic receptor in the voiding phase?
Acetylcholine
What type of neurones in the spinal cord exclusively mediate continence?
Sympathetic neurones
In the continence phase, as the bladder enlarges what happens to intravesical pressure?
Intravesical pressure increases non-appreciably

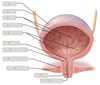
Identify structures 1-4 in the coronal section of the male bladder below:


Identify structures 5-9 in the coronal section of the male bladder below:


Identify structures 1-4 in the posterior view of the male bladder below:


Identify structures 5-7 in the posterior view of the male bladder below:

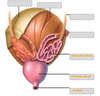
Identify structures 1-4 in the coronal section of the female bladder below:

Identify structures 5-8 in the coronal section of the female bladder below:


Identify structures 9-11 in the coronal section of the female bladder below:


What condition can β3 agonists treat?
β3 agonists can treat an overactive bladder as they act at the β3 receptors to relax the bladder (sympathetic)
What condition can α1 agonists treat?
α1 agonists treat lower urinary tract symptoms such as incontinence as they act at the α1 receptors to contract the IUS (sympathetic)
What condition can M3 antagonists treat?
M3 antagonists can treat urinary incontinence as they inhibit bladder contraction to promote urinary retention
What is the impact of spinal cord lesions from T5-T10?
- Spinal cord lesions destroy inhibitory inputs but not parasympathetic fibres so bladder is overactive
- Sympathetics keep sphincters closed so pressure increases and muscle and sphincter thicken


