S4) Basic Renal Processes Flashcards
(47 cards)
Which ion is transport together with Na+?
Cl-
How much sodium is reabsorbed in the kidney?
Up to ~99% Na+ ions, Cl- ions and H2O are reabsorbed in kidney
Sodium reabsorption varies with the ingestion of sodium.
Why?
The kidney needs to match excretion of sodium to ingestion to remain sodium balance
What happens if the amount of Na+ ions in ECF changed due to diet changes?
⇒ Amount of water in the ECF would change
⇒ ECV would change
⇒ BP would change
Sodium input only occurs through ingestion of food.
Identify 3 means of sodium output
- Sweat
- Faeces
- Urine
What is the main site of absorption in the nephron?
Proximal convoluted tubule – absorbs Na+ (67%) and H2O (65%)
What is absorbed by the following:
- Descending LoH
- Ascending LoH
- Descending thin limb of LoH: H2O (10-15%)
- Ascending thin and thick limb of LoH: Na+ (25%)
What stimulates proximal tubule reabsorption?
RAAS
Which cells are the target for aldosterone?
Principal cells of distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct
What happens when renal artery blood pressure increases?
In proximal tubule:
- Number of Na-H antiporter reduces
- Activity of Na-K ATPase reduces
What effect does an increased renal artery BP have on reabsorption?
- Pressure natriuresis:
I. Reduction in sodium reabsorption in PCT
II. Increased Na+ excretion
- Pressure diuresis:
I. Reduction in water resorption in PCT
II. Increased H2O excretion
What is the significance of the pressure diuresis and natriuresis that follow increased BP?
- ECF volume decreases
- Initial BP rise diminishes
Distinguish between paracellular and transcellular reabsorption
- Paracellular reabsorption: lumen → tight junction → capillary
- Transcellular reabsorption: lumen → apical membrane → basal membrane → capillary

Distinguish between paracellular and transcellular secretion
- Paracellular secretion: capillary → tight junction → lumen
- Transcellular secretion: capillary → basal membrane → apical membrane → lumen

What are aquaporin channels and what do they do?
- Aquaporins are channels which selectively conduct water molecules in and out of the cell
- They prevent the passage of ions/other solutes hence solely increase permeability to H2O
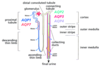
Briefly distinguish between Cl- and Na+ reabsorption
- Na+ reabsorption: active, transcellular process, driven by 3Na-2K-ATPase pumps
- Cl- reabsorption: active, transcellular and also passive paracellular process, coupled to 3Na-2K-ATPase pumps
Identify the substances that are reabsorbed in the PCT and how this is achieved
- PCT reabsorbs:
I. 65% H2O
II. 100% glucose and AA
III. 67% Na+
- Proximal tubule is highly permeable to H2O and reabsorption is isosmotic with plasma
Which 3 factors govern sodium uptake into renal capillaries in the PCT?
- Osmotic gradient established by solute absorption (osmolarity in interstitial spaces increases)
- Hydrostatic force in interstitium increases
- Oncotic force in peritubular capillary increases (loss of 20% glomerular filtrate leaving cells & proteins in blood)
Identify the 4 different transporters which facilitate sodium reabsorption in the apical membrane in S1 of the PCT

- Na-H (antiporter)
- Na-Glucose (symporter)
- Na-AA (cotransporter)
- Na-Pi

Identify the 2 different transporters which facilitate sodium reabsorption in the basolateral membrane in S1 of the PCT

- Basolateral 3Na-2K-ATPase
- NaHCO3- cotransporter (acids and bases)

Describe the movement of chloride ions in S1 of the PCT

- Urea and Cl- move down S1 compensating for loss of Glucose
- Increasing Cl- concentration creates a conc. gradient for chloride reabsorption in S2-3
How is water transported in S1 of the PCT?
Using aquaporins
How is sodium reabsorbed in the apical and basolateral membranes of S2-S3 in the PCT respectively?

- Basolateral: 3Na-2K-ATPase
- Apical: Na-H exchange

How are chloride ions reabsorbed in S2-S3 of the PCT?

Paracellular and transcellular Cl- transport