Rheum/Haem/Endo Cases AS Flashcards

B
What atypical organisms cause pneumonia?
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae•Chlamydia pneumoniae•Legionella pneumophila
- Implicated in up to 40% of CA

E
Describe a cause of microcytic anaemia.
- Haematinics
- Coeliac screen* (TTG Ab) (diagnosis confirmed on duodenal biopsy - villous atrophy)
- Remember red flags
- Top & Tail
- Order depends on upper/lower GI symptoms

Ischaemic colitis is a common cause of bloody stools in elderly

E because less than 48hours
Name 3 causes of bloody diarrhoea.
- •Infection: infective colitis
- •Inflammation: ulcerative/Crohn’s colitis (younger pts)
- •Ischaemia: ischaemic colitis (older pts)
- Malignancy
- Diverticulitis
What is a dangerous complication of ascites?
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
D
Describe 3 causes of microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia.

How can haemolytic anaemia be classified?


E
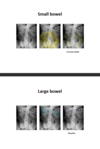
Describe the folds of the large and small bowel.
Large bowel - haustra
Small bowel - circular folds

Na should be 135-145, low urine sodium if kidneys are holding on to sodium due to ADH release.
?SIADH due to lung cancer
Therefore CXR
What is hyponatraemia? What algorithm would you use when treating them?
Hyponatraemia - EXCESS water diluting Na. Either appropriate or inappropriate.
- Appropriate if retaining more water e.g. from vomiting causing more ADH –> SIADH
- If tumour is releaseing ADH - this is inappropriate
Causes: almost always due to increased ADH
Rarer causes: excess water intake, sodium-free irrigation solutions(e.g. used in TURP).

What test is used to test for SIADH?
SynACTHen test
When will urine sodium be low in hyponatraemia?
Urine sodium will be low in hyper and hypovolaemic patients.
List some causes of SIADH.
- CNS pathology
- Lung pathology
- Drugs (SSRI, opiates, carbamazepine)
- Tumours

Beau’s lines - in chemotherapy patients when nail stops growing then grows again
Oncholysiis - nail detaches from the nail bed
List 4 causes of onycholysis.
- Trauma
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Fungal infection
- Psoriasis

A
List 3 macrovasuclar complications of diabetes.
MI/stroke/PVD
Name 3 metabolic complications of diabetes.
DKA/HHS/hypoglycaemia

D

B - LVH
Cardiac cause of collapse
Ejection systolic murmur - aortic stenosis –> hypertrophy of left ventricle

CT KUB - NON CONTRAST is very sensitive. Calculus

In malignancy ALP goes up so answer is multiple myeloma.

Fat necrosis is caused by trauma
Fibroadenoma

A
What are 4 consequences of multiple myeloma?


D
Give 4 causes of cavitating lung lesions.

What is nephrotic syndrome?
Nephrotic syndrome•
- increased permeability of GBM to protein
- Proteinura> 3g/day
- Hypoalbuminaemia
- Oedema
Explain the answer.

C. HHT - Autosomal dominant, abnormal blood vessels in skin, mucous membranes, lungs, liver, brain. Causes small mouth.

A

High prolactin supresses LH/FSH and therefore testosterone
H

Tumour is secreting prolactin and GH therefore there is excess IGF-1 production by liver
IGF-1 is measured (not GF) because GH is pulsatile
Investigation: oral glucose tolerance test shoudl suppress GH in normal people

F

E
Excess TRH can stimulate prolactin

I - blood tests would be normal


