Respiratory System Flashcards
(63 cards)
What is the function of the respiratory system?

Function of Respiratory System
Gas Exchange of the bloodstream
CO2 (out)
O2 (in)
What are the pathway organs of inhalation from start to finish?

- (Start) Nose
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachae
- Bronchi
- Lungs
- Alveoli (“air sacs”)
- *Respiratory membrane
- (Goal) Capillaries
- Contains blood
What is the name of the thin layer between the alveoli and capillaries?
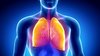
Respiratory Membrane
What are the three characterisitics of the respiratory membrane?

Characteristics of Respiratory Membrane
- Thin membrane
- Simple squamous ET = quick exchange
- Macrophages
- “Big eaters” = Pathogen eaters
- Protects membrane from pathogens (immunity)
- Surfactant-secreting cells
- Secretes lubrication
- Prevents alveoli from sticking to one another
What are the three characterisitics of a smoker’s respiratory membrane?

Smoker’s Respiratory Membrane
- Smoking kills surfactant-secreting cells
- No lubrication
- Causes alveoli to stick to one another
- Smoking kills macrophages = no immunity
- Smoking causes the thin membrane to thicken
- Causes it to be harder to breathe
What are the five steps for inhalation?

Inhalation
- Diaphragm contracts
- Moves down
- The thoracic cavity expands
- Increase in chest volume
- Lungs expand
- Increase in lung volume
- Pressure decreases in the lungs (alveoli)
- Air moves in due to pressure gradient
- From high to low pressure
What does the formula represent?
Increase Volume = Decrease Pressure

Increase Volume = Decrease Pressure
Inhalation
Air moves into the lungs due to the lungs having an increase in volume but decreased pressure
What are the five steps for exhalation?

Exhalation
- Diaphragm moves up and relaxes
- Thoracic cavity gets smaller
- Volume decreases
- Lungs get smaller
- Decreased volume in lungs
- Pressure increases in alveoli
- Air moves out of lungs due to pressure gradient
- Moves from high to low pressure
What does the formula represent?

Decease Volume = Increase Pressure
Decease Volume = Increase Pressure
Exhalation
The decreased volume of the thoracic cavity and lungs causes the pressure to increase
How do the lungs and thoracic cavity move as an unit?

Visceral pleura
The pleural cavity pulls the lungs to the chest muscles
Name

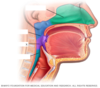
Nasal Cavity
- The nasal cavity is the inside of your nose.
- It is lined with a mucous membrane that helps keep your nose moist by making mucus so you won’t get nosebleeds from a dry nose.
- There are also little hairs that help filter the air you breathe in, blocking dirt and dust from getting into your lungs.
What is pneumothorax?

Pneumothorax = “collapsed lung”
- Pneumothorax is an air leak in the chest (hole) due to damage of the pleural membranes
What causes pneumothorax?

Causes of Pneomothorax
- A hole in the lung due to damage to the pleural membranes
- The pleural membrans holds the lungs to the chest walls

Oral Cavity
- The first section of the mouth is known as the oral cavity, or the mouth cavity.
- This space is bordered in the front and to the sides by the two alveolar arches, which contain the teeth
Name

Nostril/ External Nares
- Is one of the two channels of the nose, from the point where they bifurcate to the external opening

Larynx
- The larynx is a tough, flexible segment of the respiratory tract connecting the pharynx to the trachea in the neck.
- It plays a vital role in the respiratory tract by allowing air to pass through it while keeping food and drink from blocking the airway.
- The larynx is also the body’s “voice box” as it contains the vocal folds that produce the sounds of speech and singing

Pharynx
- The membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus.
- Food, fluid, and air “tube”

Trachea
- The trachea (or windpipe) is a wide, hollow tube that connects the larynx (or voice box) to the bronchi of the lungs.
- It is an integral part of the body’s airway and has the vital function of providing air flow to and from the lungs for respiration.

Site of Carina
- he carina is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi

Right (Main) Primary Bronchus
- The right main bronchus (primary) is one of the air passageways into the lungs
Right Lung (3 Lobes)
- Superior lobe of right lung
- Middle lobe of right lung
- Wedged shaped
- Inferior lobe of right lung

Left Lung (2 Lobes)
- Superior lobe of left lung
- Inferior lobe of left lung
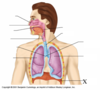
Diaphragm
- The diaphragm is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle and tendon that serves as the main muscle of respiration and plays a vital role in the breathing process

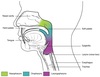
Respiratory System
- Nasel cavity
- Nostril/ external nares
- Oral cavity
- Larynx
- Right primary bronchus
- Right lung
- Pharynx
- Trachea
- Site of carina
- Left lung
- Diaphragm