Microbial Metabolism Flashcards
–Enzymes found within the cytosol of the cell
–Active inside the cell
•Endoenzymes
–Enzymes secreted by cell into environment
–Active outside the cells
•Exoenzymes
•Some enzymes need accessory molecules such as:
- Co-factor
- Co-enzyme
•inorganic helper, metal ions common, Mg++, Mn++
Co-factor (accessory molecule for enzyme)
•organic non-protein helper, NAD, FAD
Co-enzyme (accessory molecule for enzyme)

Oxygenic Photosynthesis

Holoenzyme
Type of Enzyme Activity Regulaton
–Competitive inhibition
–Allosteric (non-competitive) inhibition
–Allosteric activation
•Enzyme level regulation
Type of Enzyme Activity Regulation
–Transcription control (genetics lecture)
•Genetic level regulation

Competitive inhibition

Allosteric Inhibition

Allosteric Activation
Type of Metabolism Regulation
–If two energy sources are available, cells use the more energy efficient of the two first
–If glucose and lactose both available, lac operon off until glucose levels low
•Catabolite repression
Type of Metabolism Regulation
–Cells may synthesize molecules only as needed, cease synthesis if molecules readily available
–In trp biosynthesis, trp is co-repressor for trp operon, trp also is allosteric inhibitor for enzyme in biosynthesis
•Feedback inhibition

Feedback Inhibition
Sum of all chemical reactions occurring within a cell
Metabolism
–Series of chemical reactions mediated by enzymes
–Product of one reaction becomes substrate of the next
–Catabolic metabolism
–Anabolic metabolism
•Metabolic pathway

Metabolic Pathway
–Break larger molecules into smaller products (hydrolysis)
–Exergonic (release energy)
–ATP generated
•Catabolic pathways
–Synthesize large molecules from the smaller products of catabolism (dehydration synthesis)
–Endergonic (require energy)
–ATP consumed
•Anabolic pathways

•Energy stored in high energy bond in ATP
–Phosphorylation
•ADP made into ATP in three ways
–Substrate-level phosphorylation
–Oxidative phosphorylation
–Photophosphorylation
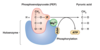
Substrate-level phosphorylation