Respiratory L3: Lung Volumes Flashcards
What are 4 factors that determine lung volume?
- Size
- Age
- Gender
- Anatomical build
What is the functional residual capacity?
How much air left in lungs after passive expiration

What is a clinical indicator of functional residual capacity?
Recoil of lungs
- Eg. decreased recoil = increased functional residual capacity

What muscle(s) affect inspiratory reserve volume?
Diaphragm

What muscle (s) affect expiration?
- Abdominals
- External intercostals

What is vital capacity?
The maximum volume of air that can be moved out during a single breath following a maximal inspiration.
- The subject first inspires maximally and then expires maximally (VC = IRV + TV + ERV).

What is the equation for vital capacity?
Vital capacity = Resting tidal + expiratory reserve + inspiratory reserve volume

What is the equation for total lung capacity (TLC)?
TLC = Residual volume (RV) + vital capacity (VC)

What is asthma? What happens to the airways?
Narrowing of smaller airways due to inflamed/thickened inner linings
Why have asthma patients an increased Residual Volume?
Decreased expiratory reserve volume= increased residual volume
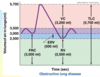
What happens in early dynamic airway closure in asthma patients?

Increased small airway resistance –> Increased loss of pressure in small airways –> Early small airway closure, decreased FVC and increased RV

Why have emphysema patients an increased Residual Volume?
Loss of lung tissue

What happens in early dynamic airway closure in emphysema patients?

Loss of lung tissue –> Decreased lung recoil –> Increased intrapleural pressure –> Early small airway closure, decreased FVC and increased RV

What happens to patients who have less compliant lungs?
In restrictive disease the lungs are less compliant and cannot be expanded as normal
- Fibrosis- scar tissue formed in alveoli walls

What happens from the start of when fresh air is inhaled?

What is the effect of dead space volume on exchange of tidal volume between the atmosphere and the alveoli?
Even though 500 mL of air move in and out between the atmosphere and the respiratory system and 500 mL move in and out of the alveoli with each breath, only 350 mL are actually exchanged between the atmosphere and the alveoli because of the anatomic dead space (the volume of air in the respiratory airways).

What is the equation for pulmonary ventilation?
pulmonary ventilation (ml/min) = tidal volume (ml/breath) x respiratory rate (breath/min)
What is the equation for alveolar ventilation?
alveolar ventilation = (tidal volume - dead-space volume) x respiratory rate
What are the different breathing patterns on alveolar ventilation?

- Deep, slow breathing- more efficient
- Not hyperventilation- shift air in and out of air

What is the Physiological dead space? How does that related to Ventilation (V) and Perfusion (Q)?
- Amount of air that doesn’t take part in ventilation V/Q > 1

Air is present but blood isn’t flowing (due to constriction of vessels = V>Q)
What is the Physiological shunt? How does that relate to Ventilation (V) and Perfusion (Q)?
- Something constricts airway and air is not present
- Blood is flowing
- Q>V
V/Q <1
Blood is present but air isn’t (due to bronchoconstriction = Q>V)

What increases first during exercise, tidal volume or respiratory rate?
The tidal volume.
- Any increase in the tidal volume will increase the alveolar ventilation by the same amount. Any increase in respiratory rate will increase alveolar ventilation by a smaller amount due to the anatomical dead space, more effort is spent to shift air in and out of the anatomical dead space without taking part in gas exchange.
alveolar ventilation = (tidal volume - dead-space volume) x respiratory rate
What is Inspiratory Reserve Volume?
The extra volume of air that can be maximally inspired over and above the typical resting tidal volume.
- The IRV is accomplished by maximal contraction of the diaphragm, external intercostal muscles, and accessory inspiratory muscles.

What is inspiratory capacity (IC)?
The maximum volume of air that can be inspired at the end of a normal quiet expiration (IC = IRV + TV).








