Reproductive System Flashcards
Introduce the ovaries
LOCATION
- •Lie in a shallow fossa,in the angle between the internal and external iliac vessels on the obturator nerve
FUNCTIONS
- •Production of female gametes (ova)
- •Synthesis of female sex hormones:
- •Oestrogens (oestradiolis the most abundant)
- •Progesterone
STRUCTURE
- paired shaped almond glands
What are the peritoneal ligaments of the ovaries?
- Ovarian ligament (ligament of the ovary) – attachment to the uterus medially
- Suspensory ligament – anchors laterally to pelvic wall (conveys neurovascular structures)
- Mesovarium– suspends the ovary in between the ovarian and suspensory ligaments

What is the histology of the ovaries?
- TUnica albuginea: germinal epithileum
- Cortex
- ovarian follicles
- somatic cells: granulosa cell + theca cells
- oogenesis: (Menstruation follicules x 3)
- Medulla

Neurovascular supply to the ovaries?
ARTERIAL SUPPLY
- •Ovarian arteries (from the abdominal aorta)
- •Pass through the suspensory ligaments
VENOUS DRAINAGE
- •A plexus of veins around the ovaries drain into the ovarian veins
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
- •Lymphatics drain into the lumbar lymph nodes
NERVE SUPPLY
- •Plexus of nerves called the ovarian plexus
- •Parasympathetics:CNX (Vagus)
- •Sympathetics:T9-11
- •Visceral afferents: enter cord at T10 level
Introduce the uterine tubes
STRUCTURE: paired muscular 10cm tube embeded in uterine wall
LOCATION
- •Extend laterally from the uterine horns and open into the peritoneal cavity near the ovaries
- •Found in the upper free margin of the broad ligament
FUNCTIONS
- •Receives oocyte from ovaries and provides a site for fertilisation
- •Nourishes the fertilized ovum and transports it to the uterus
Label the parts of the uterine tube

- INFUNDIBULUM(L.‘funnel’)
AMPULLA(L.‘flask’)
ISTHMUS(G. ‘narrow passage’)
UTERINE

Introduce the uterus
Structure: flattened pear shape organ 8x5x3 made from body and cervix
LOCATION
•Anterior to rectum, posterosuperior to the bladder
FUNCTION
•Site for reception, retention & nutrition of the fertilized ovum
Label the body of the uterus

•Fundus: regionof the uterus above where the uterine tubes enter
•
- Body: flattened in an anterior /posterior direction
- Cornu (‘horns’): where the uterus is joined by the uterine tubes
- Vesical surface (anterior)
- Related to the bladder
- Intervening vesicouterine pouch
- Intestinal surface(posterior)
- Related to coils of small intestine and rectum
- Rectouterine pouch (pouch of Douglas)
- Isthmus
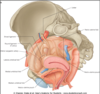
Name the parts of the neck of the uterus
Internal Os
External Os
What are the ligaments encompassing the uterus?
Round Ligament
Broad Ligament
What is the neurovascular supply to the uterus?
ARTERIAL
- •Mainly from the uterine arteriess
- •Additional supply from the Ovarian Arteries
VENOUS
- •Uterine Veins = Enter the broad ligaments with the uterine aa
- These veins drain into the Internal Iliac Veins
LYMPH
Three main routes:
- •Most vessels from uterinetubes & fundus
- •lumbar lymph nodes
- •superficial inguinal nodes
- •Vessels from the body
- •external iliac lymph nodes
- •Vessels from the cervix
- •internal iliac and sacral lymph nodes
NERVE
- Sympathetic:T12 -L1/2
- Parasympathetic:S2-4
- Visceral afferents
What are the 3 histology layers of the uterus?
- Endometrium
- •Functional layer : Undergoes cyclical changes, shed during menstruation
- Basal layer: Has stem cells that form a new functional layer
- •Uterine glands: extend the length of the endometrium
- Myometrium
- Perimetrium
Introduce the vagina
Structure: muscular membranous tube
Location: from the cervical canal to the vestibule of the vagina
Function:
- •Serves as an excretory duct for menstrual fluid
- •Forms the inferior part of the birth canal
- •Receives the penis and ejaculate during sexual intercourse
Neurovascular supply to the vagina?
ARTERIAL: vaginal artery
VENOUS: Vaginal vein + internal illiac vein via uterine vein
LYMPH:
- •Internal and external iliac lymph nodes
- •Sacral iliac nodes
- •Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
NERVE
- Uterovaginal plexus supply superior 3/4 vagina
- •Sympathetics: T12-L1/2
- •Parasympathetics: S2-4
- •Visceral afferents
- •Inferior ¼ vagina= somatic innervation
- Pudendal nerve S2-4
WHat are the main female Hormones that regulate the female cycles and where are they located
GONADOTROPHIN-RELEASING HORMONE
•From the hypothalamus
THE GONADOTROPHINS
•From the anterior pituitary gland
- •Follicle Stimulating Hormone
- Luteinising Hormone
FEMALE SEX HORMONES
•From the ovaries*
- •Oestrogens & Progesterone
- The placenta produces most sex hormones during pregnancy – more on this next year!
What’s the function of the follicle stimulating hormone in women?
- Stimulates ovarian follicle maturation
- Ovarian production of oestrogen
What’s the function of the luteinizing hormone in women?
- Triggers ovulation & formation of corpus luteum
- Ovarian production of progesterone & oestrogen
WHat the role of oestrogen in women and how is it produced?
Oestrogen:
- •Promote oogenesis, maintain the female reproductive tract, secondary sex characteristics
- •Protective cardiovascular effect
- •Maintain bone density
- Theca cells formandrogens,which are converted to oestrogens by granulosa cells
- Requires the enzyme aromatase
WHat the role of progesterone in women and how is it produced?
Progesterone
- Produced mainly by the corpus luteum
- Prepares the endometrium for implantation
- Forms a cervical mucous plug
made from cholesterol
Describe the phases of the ovarian cycle and what hormones are produced?
FOLLICULAR PHASE
- •FSH: a vesicular follicle is selected to be the dominant follicle
- •LH: oestrogens produced in large amounts by granulosa cells
OVULATION
- •High oestrogen levels a cause a spike in plasma levels of LH
- •Dominant follicle releases an oocyte into the peritoneal cavity
LUTEAL PHASE
- •Leftover granulosa & theca cells become the corpus luteum
- •Produces large amounts of progesterone and some oestrogens
- •Pregnancyvs. no pregnancy

Describe the 3 phases of the uterine (menstrual) cycle
MENSTRUAL PHASE: Endometrium sheds functional layer
PROLIFERATIVE (PRE-OVULATORY) PHASE
- •Stem cells in the basal layer generate a new functional layer
- •In response to increasing oestrogen levels produced by the maturing follicle
SECRETORY (POST-OVULATORY) PHASE
- •Begins immediately after ovulation
- •Progesterone from the corpus luteum converts the functional layer into a secretory mucosa
- •Glands enlarge and secrete nutrients to prepare endometrium for potential implantation
- •If pregnancy doesn’t occur: progesterone levels decline (corpus luteum degenerates)
- •Spiral arteries spasm:ischaemic endometrial cells undergo necrosis and slough off

What is the classification of oral contraceptives?
- Oestregen- progesterone combination
- only progesterone
How do contraceptive pills work?
- •Interferes with the hormonal axis between the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary and ovaries
- •OCP produces constant plasma levels of ovarian hormones that make the woman appear pregnant
- •Mature follicles do not develop, ovulation ceases and menstrual flow is greatly reduced (or absent)
Side effects of pills?
Common:
•nausea, breast enlargement or tenderness, weight gain, bloating and fluid retention, loss of libido, headache
Serious
thromboembolism
arterial thrombosis
Label the external female genitalia


Label the Vestibule


Introduce the clitoris
STRUCTURE V-shaped erectile organ where the labia minora meet anteriorly
•Consists of a rootand body:
- •Glans – most highly innervated, covered by a prepuce
- Two corpora cavernosa
- Two crura: connect the clitoris to the ischiopubic rami
- Covered by the ischiocavernosus muscles
FUNCTION
- •No functional relationship to the urethra
- •Organ of sexual arousal, enlarges on tactile stimulation

What is the neurovascular supply to the vulva?
ARTERIAL: External pudendal and internal pudendal artery
VENOUS: Labial veins + internal pudendal veins
LYMPH: superficial + deep inguinal nodes
NERVE:
•Sensory supply:
- •Anterior labial nerves(ilioinguinal nerve, L1)
- •Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve (L1,2)
- •Perineal branch of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S1,2,3)
- •Posterior labial nerves (pudendal nerve, S2,3,4)
•Parasympathetic supply: (S2-4)
- •Increased vaginal secretions
- •Erection of clitoris & bulbs of vestibule
Label the perineum region of the female genitalia.
identify the 2 triangles

•Diamond-shaped region located between:
- •Pubic symphysis (anteriorly), ischial tuberosities (laterally), coccyx (posteriorly)
•Can be divided by a transverse line between the ischial tuberosities:
- Urogenital triangle
- anal triangle
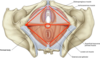
What are the layers of the female perineum ?
•From superficial to deep:
- •Skin & external genitalia
- •Superficial perineal pouch
- •Perineal membrane
- •Deep perineal pouch
- •Pelvic diaphragm
What is the content of the superficial peroneal pouch?
- •Root of the clitoris & ischiocavernosus
- •Bulbs of the vestibule & bulbospongiosus
- •Greater vestibular glands
- •Superficial transverse perineal muscles
- •Related vessels & nerves
What are the structures of the deep peroneal pouch?
- Urethra & external urethral sphincter
- Deep transverse perineal muscles
- Related vessels & nerves
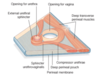
What is the peroneal membrane?
- A sheet of tough fascia that stretches between the two sides of the pubic arch
- Covers the anterior part of the pelvic outlet

What is the pelvic diaphragm and what does it consist of?
•Consists of:
- levator ani muscle group
- Pubococcygeus (PC)
- Puborectalis (PR)
- Illicoccygeus (IC)
- coccygeusmuscles (C)
- Forms the pelvic floor – separates the pelvic cavity from the perineum
- Suspended like a funnel from the pubis, lateral pelvic walls and coccyx

Describe the levator Ani muscle group?
- Pubococcygeus: arises from the body of pubis and passes back to the coccyx
- Puborectalis: a U-shaped sling that passes posterior to the anorectal junction
- Iliococcygeus: arises from the ischial spine and fascia of obturator internus, passes to the coccyx
ACTIONS
- Muscular sling that supports abdominopelvic viscera
- Elevates the pelvic floor and resists increases in intra-abdominal pressure
- Important during forced expiration, coughing/sneezing, heavy lifting
- FUNCTION: Contributes to urinary and faecal continence
- Nerve Supply:nerve to levator ani & coccygeus (S3, 4)
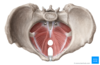
Describe coccygeus muscle?
Location: Passes from the ischial spine to the sacrum and coccyx
Action: •Forms small part of pelvic diaphragm; flexes coccyx
Nerve: somatic nerve to levator ani & coccygeus (S3, 4)

Introduce the male peroneum


