Reproductive Counseling and Gynecologic Needs Flashcards
Contraceptive methods and efficacy chart

The best way to start the conversation when a patient indicates that they want to begin birth control
What forms of contraception are you familiar with?
Most patients already know about certain methods of contraception from friends or family, and data shows that these influences are more important than a physician’s input as to the patient’s actual decision.
Relationship of epilepsy, antiepileptics, and pregnancy
- Epilepsy and antiepileptics are both individually risk factors for adverse outcomes of pregnancy
- Pregnancy itself increases the frequency of seizures in patients with epilepsy
- The hormonal profile of pregnancy interacts with many antiepileptics, reducing their efficacy and increasing their side effects
So, contraception is a big deal for patients with epilepsy. Generally speaking, it is better not to rely on condoms, or even on the pill. Copper or levonorgestrel-eluting IUDs are probably the way to go.
Contraindications to different types of IUD

Nexplanon

18 y.o. patient with cyclic migraines with aura during 3 days of her period every month and is sexually active with occasional condom use wants to discuss options for contraception.
What would likely be the best choice for this individual?
Since the migraines are likely triggered by hormone fluctuation, this patient would likely benefit from a constant hormonal profile, such an estrogen/progesterone or progesterone-only pill in 80-day (4 periods/year) or even 365-day (0 periods/year) packs.
OCP progestin summary table

Hormone excess/deficiency profiles to help address side effects when taking an OCP.

Contraindications for estrogen-containing contraception
More than one additional risk factor for stroke OR previous history of thrombotic event. These include:
- Smoking
- Migraines
- Untreated hypertension
- Obesity
- Age (cutoff is age 35)
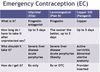
Main options for emergency contraception
Options for treatment during perimenopausal state
Patients without risk factors for stroke, breast cancer, or ovarian cancer are eligible to continue combined hormonal pills or eluting IUDs up to age 55 in order to avoid the symptoms of the perimenopau
Clinical definition of menopause
Retroactive diagnosis that can only be made after 12 months without periods, at which point the last period is designated menopause and the flanking time as “peri-menopausal”
Treating vasomotor symptoms of menopause
- SSRIs and gabapentin are both approved for prevention of vasomotor symptoms during perimenopause
- Gabapentin works especially well for nighttime vasomotor symptoms


