Aquifer Material 3 Flashcards
Common side effects of standard TB regimens
Hepatotixicity and (rarely) eye toxicity
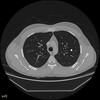
Hallmarks of a granuloma on CT
Smooth margins and central calcification are the hallmarks of residual granulomas. These are very reassuring signs for solitary pulmonary nodules, and usually indicate that cancer is unlikely.
DDx for chronic urinary retention
-
Mechanical causes
- BPH
- Prostate cancer
- Phimosis/paraphimosis
- Meatal stenosis
- Urethral narrowing (inflammation, cancer, etc)
- Bladder calculi
- Bladder tamponade
-
Functional causes
- Detrusor underactivity and/or sphincter overactivity
- Spinal cord compression/trauma, stroke, MS, Parkinson’s, damage to pelvic sphlanchnic nerves, diabetic neuropathy
- Drug-induced (anticholinergics, TCAs, antipsychotics, CCBs, levodopa)
- Detrusor-sphincter dysnergia
- Postoperative urinary retention
- Detrusor underactivity and/or sphincter overactivity
Urethral stricture
- Common cause of acute urinary retention
- AUR is an emergency and requires immediate catheterization before workup begins
- Often traumatic/iatrogenic (associated w/ catheterization), but may be post-infectious
- Sx of bladder outlet obstruction (feeling of incomplete emptying, weak stream, straining to urinate)
- Risk factor for UTI
- Diagnose w/ uroflowmetry or by visualizing on retrograde urethrography
- Treat w/ internal urethrotomy, urethroplasty, or permanent stenting
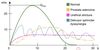
Uroflowmetry with common diseases plotted
Treatment for diabetic neuropathy of the bladder
-
Generally:
- Controlling blood glucose
-
Overactive bladders:
- Tolterodine and oxybutinin are useful for preventing bladder spasm and urinary urgency
-
Underactive bladders:
- Bethanechol helps with voiding
Bladder tamponade
Acute bladder outlet obstruction due to a blood clot at the internal urethral orifice; caused by bleeding urothelial cancer, bladder trauma, surgery (e.g., TURP), hemorrhagic cystitis or anticoagulant-induced bleeding.
Patients may complain of preceding hematuria followed by acute urinary retention.
Pharmacotherapy for BPH

Recommended preventative measures against vascular diseae for all patients with T2DM
- Smoking cessation
- Statin therapy
- Maintain blood pressure below 140/90 (lower is better, but only so far as the burden of therapy doesn’t outweight the benefits)
- Baby aspirin daily
Blood glucose target for hospitalized patients
~140-180 mg/dL
High, right? It used to be thought that lower was a good thing, but studies have shown that to be false. If you think about it, these patients probably all have elevated cortisol and catecholamines from stress while in the hospital, so they really should have a mobilized glucose response. That makes this range seem a little more normal. Plus, it is evidence-based, associated with better outcomes.
Thiazolidinedione contraindications
aka the Glitazones, a family of PPARγ agonists
They come with an increased risk of heart failure, and so are contraindicated for patients who have newly developed heart failure or NYHA class III or IV heart failure.
The receptors that TZDs activate are ubiquitous and are abundant in the cells within the renal collecting tubules. Hence, TZDs increase sodium reabsorption, leading to increased water retention. Compared to placebo, all TZDs are associated with a statistically significant increase in edema and weight.

Patient w/ long Hx of diabetes presents with foot pain from apparent diabetic neuropathy. In addition to tightening blood glucose management, how can you help this individual’s pain?
Gabapentin works well for pain associated with diabetic neuropathy
Types of diabetic retinopathy
-
Proliferative:
- Involves neovascularization of the retinal vessels or optic disc, retinal hemorrhage (dot-blot, flame), retinal fibrosis with traction detachment, and vitreous hemorrhage. Macular edema can occur as well.
-
Non-proliferative:
- Involves cotton wool spots, hard exudates, microaneurysms, and retinal hemorrhages. Vision loss usually results from severe macular edema, a thickening of the retina with resultant edema of the macula.

Contraindications of metformin
- GFR < 30
- Alcohol use
- Liver disease
- Heart failure
- Hospitilization (hold before stay due to risk of hypovolemia and contrast nephropathy)
You should consider initiating a patient w/ T2DM on insulin when. . .
. . . their HbA1c is over 10% or their glucose is regularly over 300 mg/dL, or if they have a slightly lower A1c and significant symptoms.
Glargine or detemir, the long-acting insulins, are initiated first.
Sulfa drugs
- A very diverse family of drugs that contain sulfa motifs
- Includes many antibiotics, but importantly it also includes thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, acetazolomide, sulfonylureas, previrs, sumatriptan and celecoxib (COX-2 selective inhibitor)
- Sulfamethoxazole is a classic sulfa antibiotic, specifically a bacterial antifolate
- All are capable of causing SJS and DRESS syndrome


