Biliary Pathology Flashcards
Three major signs concerning for cystic bile duct stone
- You can see a stone on ultrasound
- Clinical signs and symptoms of ascending cholangitis
- Total bilirubin is above 4
All in the context of cholestatic injury pattern on LFTs
When treating for cystic bile duct stone, you should also treat for the possibility of. . .
. . . gram negative infection of the bile duct
Often with Zoasin or ciprofloxacin/metronidazole combination to cover gram negative rods and anaerobes.
Continue until gall bladder is removed and if septic continue until symptoms subside.
Charcot’s triad vs Reynold’s pentad

DDx and initial steps based on: Patient w/ fever, colicky RUQ abdominal pain, + Murphy’s sign

Least sphlanchnic nerve
From the T12 spinal level. Follows the renal arteries to innervate the kidnies with sympathetic fibers.
Pain in this region is referred to the T12 dermatome, suprapubically.
Abdominal GI tract nerve supply

Pain in the sigmoid colon is commonly referred to. . .
. . . the inguinal or infra-inguinal region, as this is the dermatome distribution of L1-L2, the spinal origin of the sympathetic fibers that innervate the sigmoid.
Sphlanchnic nerve summary
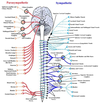
Major sphlanchnic nerves and associated spinal nervous supplies

Sympathetic visceral pain vs parasympathetic visceral pain
Sympathetic: Referred to the associated dermatome
Parasympathetic (aka vagal or sacral): Vague discomfort or nausea
How does the vagus travel down into the abdomen?
It piggybacks the esophagus until it reaches the transverse colon
Hepatocystic triangle

Mallory’s hyalinosis
Seen in chronic alcoholic hepatitis.
Precipitated microtubules.

Histologic signs of alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Steatosis (liver droplets readily visible, and in hepatocytes)
- Active acute inflammation
- Mallory’s hyalinosis
- Selective zone 3 damage and necrosis
Liver congestion on H and E
Congestion around the central veins with preserved architecture of the portal triads.
DDx of a tumor in the liver
- Metastasis (overwhelmingly)
- Choliangiocarcinoma (look like bile duct)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (usually look like normal hepatocytes, but defy normal arrangement)
Patterns of hepatic injury



