RAT 3 Flashcards
(60 cards)
optic ataxia
impaired visually guided reaching in peripheral field
where do corticospials come from
1/3 primary motor cortex 1/3 premotor/sma 1/3 post central gyrus
vertical gaze center
rostral interstitial nucleus of the MLF
horizontal gaze center
PPRF of the pons
LOTC
lateral occipital temporal cortex composed of the middle temporal gyrus (posterior middle temporal) and the lateral occipital lobe important part of the tool use network
identify

level of the inferior colliculus of the midbrain
circled is the trochlear nerve CN 4 (“egg and nest”)
- innervates superior oblique muscle (“down and out”)
- innervates contralaterally (R CN 4 innervates L superior oblique)
Identify

Level of the superior colliculus of the midbrain
identifying the oculomotor nucleus (CN III)
- innervates the medial rectus, superior and inferior rectus and inferior oblique
Identify lesion
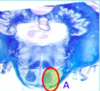
Middle alternating hemiplesia
- ipsilateral abducens issue
- contralatera T&E paralysis/weakness due to corticospinals
Identify lesion C
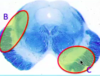
superior alternating hemiplesia
- CN III ipsilaterally
- contralateral T&E paralysis/weakness due to corticospinals
conjugate
both eyes move same direction at same rate
vergence
focus shifts between near and far objects - eyes move in opposite directions
convergence
visual axis of eyes convere (near focus)
divergence
visual axis of eyes diverge (far focus)
identify

horizontal gaze center (PPRF)
pons
identify

the vertical gaze center ( riMLF)
midbrain
identify red circle

spinal nucleus of V
pretectal area

important in pupillary light reflex; can easily identify if you see the pineal gland
near reflex
eyes converge
pupils constrict
lens round
IV innervation
contralateral superior oblique –> which pulls the eye down and out
cranial IV nerve palsy
can present with strabismus and/or compensatory head tilt; the head tilt allows for the other eye to be lined up since it cant intort, so the patients other eye will compensate by intorting the other eye and tilting her head
vestibular system
rapid estimates of head movement; cortex gives us conscious awareness
vestibular end organ
has five receptive elements
- uticle
- saccule
- three semi ciruclar canals
funciton of uticle and saccule
detect linear motions of head and orientation of head
funciton of the semicircular canal
detect rotational movement of head


