radiology of trauma Flashcards
what are direct signs of a fracture on a radiograph?
- separation sign
- radiolucent line
- look for joining of fracture lines in the mandible
- widening of the periodontal ligament space
- widening of sutures
- overlap sign
- radiopaque line
- margins may be sharp or diffuse
- abnormal linear density
- fragment displaced/rotated
- disappearing fragmanet sign
- abnormal curvature
- step deformity
- bone
- occlusal plane
- displaced bone
what are indirect signs of a fracture on a radiograph?
- soft tissue swelling
- paranasal sinus opacifcation
- fluid levels in sphenoid sinus can indicate skull base fracture
- air in soft tissues
- soft tissue
- orbital
- due to orbital floor or medial orbital floor fracture
- intracranial
- changes in occlusal plane
- le fort I fracture
- dentoalveolar fracture
- condylar neck fracture
- dental injury
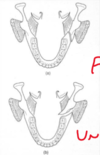
draw and name common fracture sites in the mandible
- condylar head
- coronoid process
- ramus
- angle
- body
- parasymphyseal region
- symphyseal region

what are the classic raidographic views taken if there is a suspected fracture of the mandible?
panoramic radiograph and PA mandible
lower 45/90 occlusal taken to see anteriors if needed
report radiographic findings

- LR
- two fracture lines which meet at lower border of the mandible
- shows theres a single fracture
- through lingual and buccal plates
- two fracture lines which meet at lower border of the mandible
- LR8
- widening of PDL space
- LL
- anterior
- fracture through lingual and buccal plates
describe what horizontally favourable and unfavourable mean?
in the Y axis
- horizontally favourable
- muscles keep the fragments together when they contract
- horizontally unfavourable
- muscles pull the fragments apart

describe what vertically favourable and unfavourable mean?
in the x axis
- vertically favourable
- the muscles keep the fragments together
- vertically unfavourable
- the muscles pull the fragments apart
report radiographic findings
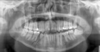
- UR
- can see change in occlusal plane - step deformity
- LR
- single fractue
- LL8
- widening of PDL
- LL
- angle of mandible
- step deformity
how should you supplement views of suspected fractures of the mandible?
with PA mandible views
take views at right angles to each other
what radiographic view is shown here
what is the finding
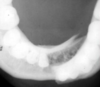
lower 90 degree occlusal
shows displacement in the horizontal plane
what radiographic view is shown here
what findings?

lower 45 degree occlusal
displacement in the vertical plane
fracture caused by mylohyoid, geniohyoid and digastric muscles - horizontally unfavourable
describe condylar fractures
- if fracture
- can be pulled by underlying muscles
- lateral pterygoid muscle
- condylar head tends to move anteriorly and medially
- can be pulled by underlying muscles
describe common occurances following fracture in the symphysial region
- fracture in symphysial region -> fracture of the condyles
- due to pull of the lateral pterygoid muscles
what fractures occur in the maxilla?
- dentoalveolar
- zygomatic complex
- le fort I, II, III
- naso-ethmoidal complex
- fractures of the orbit
what radiographic views should you request if there is a suspected fracture in the maxilla?
0 occipitomental radiograph
30 occiptiomental radiograph
submentovertex view - if suspected zygomatic arch fracture
lateral skull
always two views



