odontogenic tumours Flashcards
where do odontogenic tumours arise from?
what is the most common?
arise from epithelium within bones of the jaw
ameloblastoma is most common
what is the classification of odontogenic tumours based on?
on the stages of normal tooth development
what are the 3 groups of benign odontogenic tumours?
- odontogenic epithelium only
- only with mature fibrous stroma
- without odontogenic mesenchyme
- mixed odontogenic epithelium
- with odontogenic ectomesenchyme
- with or without dental hard tissue formation
- mesenchyme and/or odontogenic ectomesenchyme
- with ot without odontogenic epithelium
- no evidence of dental hard tissue formation
name malignant odontogenic tumours
- ameloblastic carinoma
- primary intraosseous carcinoma
- sclerosing odontogenic carcinoma
- clear cell odontogenic carcinoma
- ghost cell odontogenic carcinoma
- odontogenic carcinosarcoma
- odontogenic sarcomas
what is an ameloblastoma?
what is the classification?
benign odontogenic tumour
odontogenic epithelium without odontogenic mesenchyme
locally invasive neoplasm
- continues to grow if not removed and invade local tissues
what are the types of ameloblastoma
3 types
- solid / multicystic, intraosseous 85%
- unicystic ameloblastoma 14%
- peripheral ameloblastoma 1%
ameloblastoma clinical features
age
sex
site
- age
- wide range
- majority 4th,5th decades
- sex
- equal distribution
- site
- 80% mandible 20% maxilla
- in mandible
- 70% molar region
- mostly in angle of mandible
symptoms of ameloblastoma
- slow growing
- may be asymptomatic
- gradually increasing facial deformity and expansion of the jaw
signs of ameloblastoma
- bony, hard, non-tender ovoid swelling
- egg shell crackling of bone in advanced cases
- perforation of bone and spread into soft tissues late features
- in maxilla
- swelling may produce little swelling if extended into maxillary antrum
what are the radiographic features of an ameloblastoma
- multilocular mostly
- well defined corticated outline
- uniformly radiolucent
- radiopaque septa
- effect on adjacent structures
- expansion of buccal/lingual bone
- teeth displaced
- roots of involved teeth may be resorbed
- may be associated with unerupted tooth, particularly lower third moalrs mimicking dentigerous cyst
what radiographic features are shown here
identify this

- multilocular appearance
- angle of the mandible
- resorbing distal root of lower 2nd molar
- displacement of 3rd molar
ameloblastoma
what radiographic features are shown here
identify

- radiolucency at angle of the mandible
- involving ramous
- resorption of the roots
- multilocular appearance
ameloblastoma
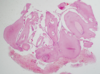
what are the different patterns of histopathology in ameloblastoma
follicular or plexiform
describe the follicular pattern of histopathology in an ameloblastoma
- rounded islands or follicles
- surrounded by fibrous tissue
- resembling enamel organ of tooth germ
- central mass resembling stellate reticulum
- periheral layer resembling ameloblasts
- nuclei of peripheral cells show reverse polarity

what is reverse nuclear polarity?
nuclei are polarised to the opposite end of the cell to the basement membrane

describe the plexiform histology of an ameloblastoma
- tangled network of
- anastamosing strands
- irregular massess
- peripheral layer of ameloblast like columnar cells with central stellate reticulum like cells
- cyst formation common but due to stromal degeneration

what is the treatment for an ameloblastoma
- solid/multicycstic ameloblastoma
- surgery essential
- high recurrence after curettage
- complete resection with margin of normal bone
- radio and chemotherapy is insensitive
- mxaillar tumours are often more destructive
- long term follow up required
- recurrence > 10 years post op
what is an adenomatoid odontogenic tumour?
what is the classification?
duct like structures
slow but progressive growth
odontogenic epithelium without odontogenic ectomesenchyme
what are the clinical features of an adenomatoid odontogenic tumour
age
sex
site
- age
- 2nd/3rd decades of life
- sex
- F>M
- site
- maxilla 2x more than mandible
- canine area + anterior part of maxilla mostly
what are the symptoms and signs of adenomatoid odontogenic tumour?
- symptoms
- slowly enlarging painless swelling
- signs
- often associated with unerupted tooth
- rare extra-osseous lesions
- usually anterioe mxillary gingiva
what are the radiographic features of an adenomatoid odontogenic tumour?
- well defined radiolucency
- unilocular, often surrounding whole tooth
- corticated outline
- radiolucent, calcification may produce faint radiopaicities
- may mimic dentigerous cyst
what radiographic features are present here?
identify

well defined radiolucency
unilocular & surrounding the whole tooth
corticated outline
simialar to dentigerous cyst
adenomatoid odonteogenic tumour
describe the histology of an adenomatoid odontogenic tumour
- well encapsulated
- whorled masses of epithelium
- columnar cells form duct-like structures with eosinophilic material in central spcaes

what is the management for an adenomatoid odontogenic tumour?
is benign
readily enucleated
does not recur