Forceps in exodontia Flashcards
(26 cards)
Draw a table to outline which instruments are used on which teeth

Describe instrument No.2 in terms of :
- beak design
- direction of forces
- what teeth
- Beak design:
- Serrated to improve grip
- Concave to fit around tooth
- In long axis of handle – easy access
- Direction of forces:
- Apical
- Rotational
- Used for:
- Upper centrals, laterals, canines

Describe instrument No.73 in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
- Beak design:
- Pointed to engage furcations
- Concave to fit tooth surface
- 90° to handle
- Direction of forces:
- Apical
- Bucco-lingual
- “Figure-of-8”
- Used for:
- Lower molars

Describe instrument No.74 in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
Beak design:
- Concave to fit root surface
- Long beak to reach roots
Direction of forces:
- Apical
- Rotational
- Bucco-lingual
Used for:
- Lower roots

Describe instrument No.76 in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
Beak design:
- Concave to engage tooth surface
- 30° cant
Direction of forces:
- Apical
- Bucco-lingual
- (Rotational forces can be used for the upper second premolar ONLY)
Used for:
- Upper premolars

Describe instrument No.94 in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
Beak design:
- Pointed buccal beak to engage furcation
- Curved to fit tooth surface
Direction of forces:
- Apical
- Buccal
Used for:
- Upper right molars

Describe instrument No.95 in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
Beak design:
- •Pointed buccal beak to engage furcation
- •Curved to fit tooth surface
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Buccal
Used for:
- •Upper left molars
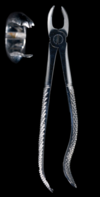
Describe bayonets in terms of :
beak design
direction of forces
what teeth
Beak design:
- •Elongated for better access
- •Angled for better access
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Bucco-palatal
Used for:
- •Upper 3rd molars

what is the operator positioning for extractions in the lower right quadrant?
- operator
- behind patients right shoulder
- broad stance
- straight back
- patient
- ’s mouth is at elbow level
what is the operator positioning for extractions in the lower left, upper left and upper right quadrants?
- operator
- facing patient on patient’s left
- broad stance
- straight back
- patient
- ’s mouth at elbow level
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of a lower right?
- index
- buccal side of root area
- thumb
- lingual side
- middle finger
- mandibular border - extraorally
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of a lower left?
- index
- support tooth buccally
- thumb
- mandibular border extraorally
- middle finger
- lingually tooth
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of a lower anterior?
- index
- tooth labially
- thumb
- mandibular border extraorally
- middle finger
- lingually
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of a upper right?
- standing behind patient
- index
- palatally
- thumb
- buccally
- make a fist with hand
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of a upper left?
- index
- tooth buccally
- thumb
- palatally
- make fist
how is the left hand placed whilst extraction of an upper anterior?
- index
- tooth labially
- thumb
- palatally
describe extraction of the upper incisors in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
No.2
Root morphology:
- •Conical
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Rotational
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the upper canines in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
No.2
Root morphology:
- •Conical
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Bucco-palatal
- •Rotational
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the upper premolars in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
No.76
Root morphology:
- •Oval; broadest bucco-palatally
- •1st premolar 2 roots
- •2nd premolar 1 root
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Bucco-palatal
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the upper molars in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
No.94/95
Root morphology:
- •2 buccal roots
- •1 palatal root
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Bucco-palatal
Path of delivery:
- •Buccal
describe extraction of the upper 3rd molars in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
bayonets
Root morphology:
- •Usually follows first and second molars
- •Can be varies
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Buccal
•“Figure-of-8”
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the lower incisors in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
no.74
Root morphology:
- •Oval; broadest bucco-lingually
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Bucco-lingual
- •Rotational
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the lower canines in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
no.74
Root morphology:
- •Conical
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Rotational
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal
describe extraction of the lower premolars in terms of :
instrument
root morphology
direction of forces
path of delivery
no.74
Root morphology:
- •Conical
Direction of forces:
- •Apical
- •Rotational
Path of delivery:
- •Incisal


