RAD02 - Lecture 6 - Occlusal Flashcards
(26 cards)
Define occlusal radiography (1)
Intra-oral technique where the image receptor (i.e. film packet or phosphor plate) is placed on the occlusal plane
Can you use solid state sensors for occlusal radiographs?
No
What are the 5 different types of occlusal radiographs?
Maxillary
Upper standard
Upper oblique
Mandibular
Lower 45o
Lower 90o
Lower oblique (just same as upper oblique but for lowers)
What are the 2 image receptors that can be used for occlusals?
Phosphor plate
Film packet (size 4)
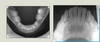
Identify the type of occlusal radiograph - what is it showing?

Upper Standard Occlusal -> anterior maxilla (upper anteriors)

What are the clinical indications for Upper Standard Occlusals? (5)
Evalute size/extent of lesions (i.e. cysts, tumours) -> anterior maxilla
Peri-apical of anterior maxilla teeth (for patients who cant tolerate PAs)
Orthodontics -> detects presence of unerupted canines, supernumaries, odontomes
As a mid-line view when locating unerupted canines, supernumeraries, odontomes
Dento-aveolar trauma -> anterior maxilla
Describe the technique for Upper Standard Occlusal (5)
1) Seat patent with head supported and occlusal plane horizontal
2) Use protective thryoid shield
3) Insert image receptor flat into the mouth (so its on the occlusal surface of the lower teeth)
4) Tell patient to bite genetly together
5) Position the X-ray tubehead above the patient at the midline
6) Angulate the tubehead at a 65-70o downwards through the bridge of the nose -> image receptor
Identify the 8 structures that should be shown in an upper standard occusal (anterior maxilla)


How is the technique for Upper Standard Occlusal modified for children? (2)
Use small size 2 phosphor plate or film
Angulation of X-ray tube-head -> 50o

Describe the quality criteria for Standard Upper Occlusals (7)

Apices of upper incisiors clearly defined
Unerupted canines (if present) - crows and apices
First and second molars should be included
Right and left should be comparable
Minimal elongation/foreshortening***
No geometrical distortion (from incorrect angulation or film bending)***
Contrast and density should allow you to differentiate -> enamel, dentine, pulp***
*** -> same for all occlusal radiographs (except contrast/density for 1)
Identify the type of occlusal radiography

Upper Oblique Occlusal - posterior maxilla (upper posteriors)
Describe the technique for Upper Oblique Occlusal (6)
1) Seat patent with head supported and occlusal plane horizontal
2) Use protective thryoid shield
3) Insert image receptor flat into the mouth (with long axis antero-posteriorly to the side of the mouth under investigation)
4) Tell patient to bite genetly together
5) Position the X-ray tubehead to the side of the patients face
6) Angulate the tubehead at a 65-70o downwards through the cheek -> image receptor

Describe the quality criteria for Upper Oblique Occlusals? (6)
Apices of upper posterior teeth being investigated clearly defined
All posterior teeth on one side should be included
Antral floor should be shown
- Minimal foreshortening/elongation*
- No additional geometrical distoration (from incorrect angulation/film bending)*
- Contrast and density should allow differentiation -> enamel, dentine, pulp*
Identify the 5 structures that should be shown in an upper oblique occusal (posterior maxilla)


Identify the type of occlusal radiograph

Lower 45o Occlusal
What are the clinical indications for Lower 45o Occlusals? (4)
Dento-alveolar trauma -> in conjunction with PAs
Evalulation of the size and extent of lesions -> anterior mandible
Peri-apical -> anterior mandible teeth (for people who cant tolerate PAs)
Vertical displacement of fractures -> anterior mandible
Describe the technique for Lower 45o Occlusals (5)
1) Seat patent with head supported and occlusal plane horizontal
2) Insert image receptor centrally into the mouth (with long axis antero-posterioly or crossways)
3) Tell patient to bite genetly together
4) Position the X-ray tubehead at the midline
5) Angulate the tubehead at a 45o upward through the chin -> image receptor

Describe the quality criteria for Lower 45o Occlusals (5)
Apices of lower incisor teeth should be clearly defined
Lower border of the mandible should be shown
- Minimal foreshortening/elongation*
- No additional geometrical distoration (from incorrect angulation/film bending)*
- Contrast and density should allow differentiation -> enamel, dentine, pulp*
Identify the 3 structures that should be shown in a lower 45o occlusal (anterior mandible)


Identify the type of occlusal radiograph

Lower 90o Occlusal
What are the clinical indications for Lower 90o Occlusals? (6)
Detection of calculi in the submandibular duct
Bucco-lingual expansion of lesions (affecting mandible)
Bucco-lingual position of unerupted teeth (including wisdom)
Mandibular tori
Horiztonal displacement of fractures
Implants (assessment)
Describe the technique for Lower 90o Occlusals
1) Insert image receptor centrally into the mouth (with long axis antero-posterioly or crossways)
2) Tell patient to bite genetly together
3) Tip patients head backwards (as far as comfortable)
4) Position the X-ray tubehead below the body of the mandible (in the side of interest)
5) Angulate the tubehead at a 90o upward through the chin/neck -> image receptor

Identify the 4 structures that should be shown in Lower 90o Occlusals


Describe the quality criteria of lower 90o occlusals (4)
First molar teeth should be included
Body of the mandible on each side should be equidistant (equal distance) from the midline (appears symmetrical)
Contrast and denisty will depend on the cinlical indication - i.e. demonstrate salivary calculi -> soft tissue exposure should be used