RAD02 - Lecture 1 - Periapicals (PA) Flashcards
What does intra-oral radiography require? (3)
Conventional dental X-ray generating unit
Image receptor (inside the mouth)
Patient
What are the 3 main types of image receptors?

Solid state recepetors (intra- and extra-oral)
Use CCD (charge coupled device) or CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) sensors
The sensors are connected directly to a computer producing -> instant images
Problems - intra-oral sensors are quite bulky (difficult to position)
Phosphor plate receptors - 0, 1, 2 (PAs) (intra-oral)
Needs to be packaged first
It captures the image then needs to be scanned -> reader (i.e. Digora Optime)
Film packets - size 4 (occlusal), size 2 and 0 (PAs)
Not used in Guy’s but still used in many dental practices
Describe the radiograph produced by phosphor plate or solid-state receptors (3)
Black, white, grey digital radiograph (256 shades of grey in typical digital image)
Made up of pixels -> (small = ↑ better resolution)
Each pixel is assigned a shade of grey depending on amount of radiation that has reached that part of the sensor
How is resolution measured? (1)
Pixel size (smaller pixels = ↑ resolution)
Compare the resolution of solid state and phosphor plate receptors (2)
Storage phosphor plate -> pixel size = 60-70μm
CCD (solid state sensor) -> pixel size = 20-70μm
Give an example of another measurement of resolution (aside from pixels) (1)
Spatial resolution -> Line pairs/mm
Compare the spatial (line pairs/mm) between direct-action packet film, indirect-action film/screen combination, digital systems (3)
Direct-action packet film -> 10-20lp/mm
Indirect-action film/screen combination -> 5lp/mm
Digital systems -> 7-25lp/mm
What can be altered to enhance a digital image using computer software (i.e. romexis)?
Brightness
Contrast
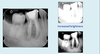
What is Peri-apical (PA) radiography? (4)
Intra-oral technique designed to show:

Individidual teeth (from root to crown)
Tissues around the apices (5mm surrounding bone)
No overlap of adjacent teeth
No elongation or foreshortening
What technique is used to take PAs? (3)
Paralleling

Image receptor is placed parallel to the long-axis of the tooth (should be in contact***)
X-ray beam is also parallel - meeting both the tooth (object) and image receptor at right angles
Clinically how can you position the image receptor so its parallel to the tooth and in contact?

You cant - because of the anatomy of the mouth
The only way to make them parallel is by having them positioned some distance apart

What is the problem with there being distance between the image receptor and the tooth (no contact)? (3)

Magnification
This can be either:
Extensive -> using a short Fsd w/ diverging beam
Minimal -> using a long Fsd w/ parallel beam *****
Fsd = focal spot to skin distance (200mm)

Explain the effects of changing the position of the object, image receptor or x-ray beam (3)
Changing position of the tooth (but image receptor + x-ray beam parallel) -> foreshortening
Changing position of the image receptor (but tooth + x-ray beam parallel) -> elongation
Changing position of the x-ray beam (but tooth + image receptor parallel) -> distortion

Describe how a PA is taken (5)
1) Prepare phosphor plates -> place in correct packet (size 0 -> lower incisors, size 1 -> upper incisors, size 2 -> posterior)
2) Set up holder - using the correct bite block (blue = anterior, yellow = posterior), metal arm and aiming ring
3) Place plate onto holder (anterior -> long axis vertical, posterior -> long axis horizontal) and insert into the mouth
4) Align tube head with notches on aiming ring
5) Take radiograph
What teeth should be taken in the same PA radiograph? (3)
Maxillary anterior (size 1) - 3, 21, 12, 3
Mandibular anterior (size 0) - 32, 11, 23
Posterior (size 2) - 87, 654, 456, 78
Why cant you take maxillary anteriors together using a size 1 film?
Because the nasal septum/nose will be in the way
How does the technique differ using a solid-state sensor compared to phosphor plate for intra-oral radiograph? (1)
A barrier sheath is required for infection control

What are the advantages of the paralleling technique? (6)
Crowns, roots, periodontal bone levels are well represented
Geometrically accurage images with minimal magnification
Minimal elongation or foreshortening
Aiming ring helps position the X-ray tubehead correctly
X-ray beam aimed at the centre of the image receptor -> no coning off or cone cutting
Images are reproducible at different visits and by different operators
What are the disadvantages of the paralleling technique? (6)
Position of the image receptor can be uncomfortable (can even cause gagging especially with solid state -> bulky)
Positioning holders can be difficult for inexperienced operators
Anatomy of mouth can make the technique impossible (i.e. flat, shallow palate)
Positioning holder in lower third molar region -> difficult
Technique is impossible for very small children
Technique needs to be modified during endodontics
What is the criteria for image quality of PAs? (6)
Crown and entire roots of tooth/teeth under investigation need to be in image
Apical tissues clearly defined (including full extent of any disease)
Minimal vertical geometrical distoration
No overlapping
No unwanted superimposition of adjacent structures
Contrast and dentisty should allow you to differentiate between enamel, dentine and pulp
What are the 3 ratings you give to quality of digital radiographs?
1 (excellent) - no errors of patient preparation, positioning or digital receptor handling (*)
2 (diagnostically acceptable) - some errors of (*)…but doesnt detract from diagnostic utility of the iamge
3 (diagnostically unacceptble) - errorrs of (*)… or exposure (which cant be corrected by software) making it diagnostically unacceptable


