RAD02 - Lecture 4 - Panoramic (DPTs) Flashcards
(30 cards)
What does DPT stand for?

Dental panoramic tomography (radiography)
What are the common clinical indications for DPTs? (6)
Bony lesion or unerupted tooth is a size or in a position that precludes (prevents) its complete demonstration on intra-oral radiographs
Grossly neglected mouth
Orthodontic assessment
Third molar assessment (to planned intervention)
Mandibular fractures
Periodontal assessment if pocketing >6mm in >1 quadrant
Give 4 examples of other indications for DPTs
Prior to surgery under GA
Assess multiple sites for implants on ajaw
Patients who cannot tolerate intra-oral radiography
TMJ assessment (to exclude bone disease)
Give 2 examples of where DPTs cannot be justified
No clinical signs or symptoms
For review at arbitary (personal) time intervals
What should you consider first prior to DPTs - why?
Intra-oral radiographs -> lower dose and better detail
How is a simple linear (flat) tomograph produced?
Moving the X-ray tube in one direction and the film in the opposite direction (on either side of the patient)

What is the shape of the panoramic focal trough (or in focus layer)? (1)
3D horse-shoe shape

What determines the precise shape and positon of the “in focuse” horse-shoe layer? (2)
Its predetermined by the manufacturer
Thus - positioning of the patient correctly within the machine is crucial

What happens to any teeth that lies outside the focal trough? (1)
Appear burred and out of focus (on the film)
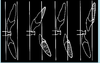
This happens when you have abnormal incisior position -> it will be impossible for patient to bite both U and L incisiors into the peg at the same time
How would the image differ if the object is inside or outside the horseshoe?
Inside horseshoe = object is further from image receptor -> ↑ distance (d) -> appears bigger + wider
Outside horseshoe = object is closer to image receptor -> appears smaller + narrower

How long does it take for the machine to orbit around the head?
15-18 seconds
Does the X-ray machine move behind the patients head? (1)
Yes
What is the beam of X-rays shape? (1)
Narrow vertical slit
What is the angulation of the X-ray beam? 91)
~8o upwards

What is the equipment needed to take a DPT? (2)
X-ray tube head
Cassette + phosphor plate

How is the image formed (with regarding the film/phosphor plate)? (2)
The film/phosphor plate is exposed bit by bit throughout the movement
As the vertical beam traverses across the image receptor

With regard to the distance between the focus layer + film - what is the magnification of DPTs?
x1.3 magnification
What should you do to reduce radiation dose when taking DPTs? (2)
The smallest field size compatible with obtaining the required information should be used
This ensures that only pre-selected parts of the patients are exposed and imaged ont he final film

What are the 6 typical field size options?
Full field
Dentition only (doesnt include condyles or upper part of maxilla)
Maxilla only
Mandible only
Additional subdivisions (i.e. right/left side or specific quadrants)
TMJ (condyles can be image with mouth close and open)
If you just choose the field size for dentition (only) - how much does the radiation dose decrease by from a full field?
50% reduction in effective dose
What are ghost shadows? (1)
Shadows of structures on the opposite side of the jaw
How can you spot ghost shadows? (3)

Out of focus (not in the focal trough)
Magnified (further away form the film than focal trough)
Projected higher (upward angulation of x-ray beam)

Describe how you would prepare a patient for a DPT (12)
1) Confirm patients identity
2) Remove anything radio-opaque between -> top of ears and shoulders (i.e. earings, necklace, nose studs, tongue studs, hair slides, glasses, hearing aids)
3) Remove denture and orthodontic appliances
4) Explain procedure and equipment
5) Position patient in the machine -> hold handles
6) Ensure patient spine is straight (if standing or seated)
7) Get patient to bite their upper and lower incisiors edge-to-edge on the bite peg
8) Ensure chin is in good contact with chin support
9) Immobilise the head using the temple supports
10) Use the light beam markers as a guide to adjust head position (mid saggital, frankfurt, canine line) and keep straight w/ no rotation
11) Ask patient to remain still
12) Press exposure button

GIve examples of patients that are not suitable for DPTs
Unable to keep still (physical or mental disabilities)
Unable to support themselves
Physical deformity (i.e. kyphosis)
Small children



