RAD02 - Lecture 5 - Film-based imaging and Chemical processing Flashcards
(22 cards)
What are the 3 speeds of intra-oral radiographic film?
E
D
F

What side of the film packet should be facing the X-ray beam?
White surface
(the opposite side will be white + another colour -> picture)

What is the contents of a intra-oral radiographic film packet? (4)
Outer wrapper -> white side / coloured side
Plastic film (coated on both sides in green emulsion)
Black paper (either side of film)
Lead foil (thin sheat)

What happens to the image if you use the film packet the wrong way round?
Image becomes pale

Define chemical (film) processing
Events required to convert the invisible latent image -> visble black/white radiographic image
What are the 2 types of chemical processing?
Manual (wet)
Automatic

Explain how a film changes after being chemical processed (image)

What are the 3 key x-ray set variables on the control panel?
kV - voltage
Time - secconds
mA - current

What is the function of Kv (voltage)? (3)
Determines the energy/penetrating power of the photons
This is known as the quality of X-ray beam
This effects the film contrast

What is the function of mA (current) and time (secs)? (2)
Determines quantity of X-ray photons
This effets the degree of blackening of film

In terms of grading (1,2,3) - what percentagest should dentists target for? (3)
Grade 1 - 70% ≥
Grade 2 - ≤ 20%
Grade 3 - ≤ 10%
Identify the exposure/processing error (3)

Too dark
Over-exposed (time set too long/faulty timeer)
Over-developed (temp or concentration too high, develop time too long)
Identify the exposure/processing error (3)

Too pale
Under-exposed - time too short, faulty timer
Underdeveloped - temp or concentration (dilute) too low, develop time too short/exuasted
Identify the exposure/processing error (3)

This occured during wet processing (as opposed to automatic)
Developer level too low -> no blackening of upper part of film
This leads to it being completely cleared in the fixer
Identify the exposure/processing error (1)

Fixer splashes
Identify exposure/processing error (1)

Under-fixed
What makes it obvious that this “pale film” is not due to under-exposed/developed - and more to do with handling error?
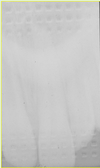
You can see the pattern of the lead foil
This means the film is back to front

Identify the cause of handling-error (1)

Exposure to light (fogging)
Identify the cause of the handling error

Film bent -> causes pressure to form a dark line

Identify the cause of the handling-error (1)

Finger nails damage the film emulsion -> black pressure marks
Identify the handling-error

Film used twice -> double exposure
Identify the exposure/processing error (1)

Film left in final wash for too long


