Pseudocysts Flashcards
(53 cards)
What are pesudocysts?
- They have no epithelial lining.
- They’re called cysts by convention just because that’s what everybody is used to
- They’re not true cysts.
pesudocysts
List
(5)
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
- Antral Pseudocyst
- Simple Bone Cyst
- Osteoporotic Bone Marrow Defect
- Stafne Bone Cyst
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Demographics
■ Most common site in the body is long bones or vertebrae
_■ In the jaw_s, most frequently seen in the 1st and 2nd decade
■ MD > MX
it’s a pesudocyst
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Clinically
- swelling, frequently a rather rapid swelling
- often with pain and/or paresthesia (signs which can be suggestive of the presence of a malignant or aggressive lesion)
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Etiology
- Etiology is unclear, may result from trauma or a vascular malformation
- most agree that it is a reactive and *not* a neoplastic lesion
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Radiographically
■ a radiolucency which can be either unilocular or multilocular in appearance
■ Borders are variable, often irregular in shape and may be ill-defined (again, giving the suggestion of malignancy)
■ Teeth may be displaced
■ we may see cortical expansion and thinning ~ the cortex itself can become quite thin
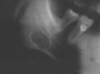
What does this person have?

- you might think that he has an odontogenic infection but he didn’t. You can see that there’s
a pretty significant swelling on the left side of his face
This is a Aneurysmal Bone Cysts

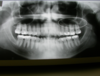
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
you can see that there is kind of a
multilocular radiolucency in this particular area

Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
✎ There’s a radiolucency involving the second molar
that’s going as far anterior as the first molar and back
to the third molar
✎ There is a little bit of spiking root resorption and
that’s one of the signs that we associate with
malignancy
✎ It’s a little bit ill-defined ~ hard to say exactly
where it begins and ends
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
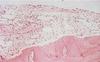
Histology
■ An intraosseous accumulation of variously sized blood filled sinusoidal spaces (not lined by endothelium)
surrounded by cellular fibroblastic tissue
■ Woven (reactive, immature) bone may be seen in the FCT
■ Gross appearance of a “blood soaked sponge”
■ The connective tissue can contain multinucleated giant cells and extravasated red blood cells

Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
✎ It looks like a blood soaked sponge
✎ There’s these open sinusoidal spaces and then fibrous connective tissue surrounding them.
✎The sinusoidal spaces can vary in size; some of them are fairly small and others are large
Wall of the aneurysmal bone cyst can have a histology similar to the following
✎ Central giant cell granuloma
✎ Cherubism
✎ Brown tumor of hyperparathyroidism

Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Histology
Left Image: you can see some of them are fairly small, little spaces within the connective tissue and others are large
✎ at the edges, you do not see endothelia lining, so
these are not vessels neither veins or arteries because they’re not endothelia lined
✎They are just these spaces within this fibrous connective tissue, referred to as sinusoids. You can see that there’s bone trabeculae down here on the left
Middle: On high power, there’s multinucleated giant cells (red) within the fibrous connective tissue and then there’s extravasated red blood cells within the connective
tissue
Right: On higher power; (red) would be the lumen of those sinusoidal spaces. Below that is the connective tissue and you can see there’s no endothelia lining, there’s just fibrous connective tissue and then some
multinucleated giant cells
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
Treatment
■ Treatment is surgical enucleation and curettage
■ lesions can recur ~ Usually the recurrence is because
you didn’t get the entire thing out the first time around
■ Some surgeons follow enucleation with cryotherapy
■ Irradiation is contraindicated
Is bleeding a concern during surgical removal of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst?
■ No, vascularity is predominantly “low flow”, therefore not as much concern for bleeding upon surgical removal
■ As compared with central hemangioma where there is a concen for bleeding
Antral Pseudocyst
They are different than surgical ciliated cyst
in their lining, etiology, location and appearance!
As opposed of surgical ciliated cysts, Antral psuedocysts are not —-
( in term of their lining)
Not epithelial lined spaces
As opposed of surgical ciliated cysts, Antral psuedocysts are not —-
( in term of location)
Not within the bone but are in the sinus
As opposed of surgical ciliated cysts, Antral psuedocysts Develop as —-
( in term of etiology)
develop as an accumulation of an inflammatory exudate (often serum) between the sinus epithelial lining and the bone
-It develops because of an inflammatory event in the jaw, usually the maxilla, often from the roots of the maxillary teeth that cause inflammation
As opposed of surgical ciliated cysts, Antral psuedocysts appear as —-
( in term of Radiology)
Appears as a dome shaped elevation of the floor of the sinus
Antral Pseudocyst
- a Dome-shape swelling on the floor of the sinus.
- They can sometimes be fairly subtle
Antral Pseduocyst are NOT Mucoceles
Mucoceles would have more of meniscus-like
appearancewhere it would come up tothe edge of
the sinus

Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
✎ A dome shape swelling on the floor of the sinus that’s associated with some _sort of inflammation of tooth of t_he premolar caused inflammation underneath the apex of the bone (right) and then that leads to accumulation of fluid which causes the sinus lining to elevate off the bone and fill with fluid
✎ After root canal therapy and once the infection gets under control, these will typically resolve on their own
Simple Bone Cyst
also known as
aka traumatic bone cyst
Simple Bone Cyst
Charcterstics
- A benign, empty or fluid filled, cavity in bone which is devoid of an epithelial lining – a pseudocyst
- Thought to be reactive, NOT neoplastic