Non Odontogenic Cysts COPY Flashcards
Fissural Cysts
(6)
❑ Nasolabial cyst
❑ Globulomaxillary cyst (historic)
❑ Nasopalatine (incisive canal) cyst
❑ Incisive papilla cyst
❑ Median palatal cyst
❑ Median mandibular cyst (historic)
where a number of the visual cysts would develop

(1) That’s the nasopalatine, which is sort of up in the labial nasal fold and it’s in the soft tissue.
(2) Sort of where the nasal alveolar cyst would occur.
(3) Where the globular maxillary cyst would occur between the canine and the lateral sometimes between the lateral and the first premolar
(4) The nasopalatine in the cyst of the nasopalatine papilla
(5) Is the median palatal
Nasolabial Cyst
also known as
aka Nasoalveolar cyst
Nasolabial Cyst
Etiology
■ Thought to be caused by:
- either epithelial remnants of the nasolacrimal duct
- or cells left after fusion of the maxillary, medial and lateral nasal processes during development of the midface
Nasolabial Cyst
Location
Rare soft tissue cyst of the upper lip, lateral to the midline (right under the ala of the nose) *NOT in bone*
■ Clinically see a swelling which can cause elevation of the ala of the nose ■ Intraorally see a swelling in the maxillary vestibule lateral to the midline (usually sort of in the canine area or just a little bit distal to the canine area) ■ Pain is uncommon, unless cyst becomes infected
Nasolabial Cyst
Clinically & Intraoray
■Clinically we see a swelling which can cause elevation of the ala of the nose
■ Intraorally see a swelling in the maxillary vestibule lateral to the midline (usually sort of in the canine area or just a little bit distal to the canine area)
■ Pain is uncommon, unless cyst becomes infected
Nasolabial Cyst
Demographics
■ Peak in 4th and 5th decades
■ 3 to 4 times more common in females
■ ~ 10% of cases are bilateral
Nasolabial Cyst
Treatment
- Surgical Excision via intraoral approach,
- usually do not recur ~ very low risk of occurrence
_Nasolabial Cys_t has a a respiratory type epithelium and so it’s very similar to what you would see in ?
either in the sinus or in the nasopalatine ducts
What is this clinical finding?

Nasolabial Cyst
The lesion here just below the nose and you can tell that it’s sort of raising the edge of the nose slightly
What is this clinical finding?

Nasolabial Cyst
the lesion raising the edge of the nose slightly
“Globulomaxillary Cyst”
Origin controvesy
why the name in quotations?
- it’s in quotations, because really there is no such thing as a globulomaxillary cyst
- because it was thought that this was remnants after fusion of the globular portion of the nasal process with the maxillary process, and now we know that these two processes are always united from the start and that there is no fusion
- When biopsied these cysts are odontogenic in origin
what does it mean for Globulomaxillary Cyst to be odontogenic in origin?
✎This is term used to describe a cyst in a particular anatomic location it is not a diagnosis
✎An odontogenic cyst (inflammatory cyst, lateral periodontal or even sometimes OKC) that forms in the area between the maxillary lateral incisor and the canine roots
~ It’s really associated with a_n anatomic location not with any particular cyst._
✎So it can be any of the odontogenic lesions such as lateral granulomas or cysts, OKCs, COCs, etc.
Globulomaxillary Cyst
Radiographically
✎Presents as a “inverted pear” shaped well-circumscribed radiolucency
✎Frequently causes displacement of the roots
Is this

Globulomaxillary Cyst
lateral granulomas
OKCs
COCs
- we can see the displacement of the root
- A teardrop or pear shaped radiolucency between the lateral and the canine
- Well circumscribed maybe leaving a little sclerotic edge up here
- ended up being in a odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)
Is this Globulomaxillary Cyst , lateral granuloma or OKC?

~ it is kind of a teardrop or pear shaped size
~Little less well differentiated in this particular instance but again unilocular radiolucency between the roots of two teeth
This one ended up being an OKC
Most common non-odontogenic cyst of the oral cavity
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
also known as
incisive canal cyst
nasopalatine canal cyst
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Origin
- arise from epithelial remnants of the nasopalatine duct which, embryologically, connects the oral and the nasal cavities
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Demographic and Location
- Peak presentation in the 4th to 6th decades, but can occur at any age ~ because it takes a little bit of time for the cyst to grow within the bone
- commonly found on the anterior palate ~ typically in the nasal area of the papilla.
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Clinically
■ present with swelling o_f the anterior palate_ (in the nasal area of the papilla)
■ Most are asymptomatic, but they may have pain or drainage
What are two different ways nasopalatine duct cyst arise?

- *A**. It can either be the cyst totally within bone
- *B**. It can actually cause widening of the orifice and causing the soft tissue expansion in this way
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Radiographically
■ a well-circumscribed unilocular radiolucency on the midline of the anterior hard palate
between and apical to the central incisors
■ The radiolucency often have an oval or inverted pear shape with a sclerotic border
■ Superimposition with the nasal septum can create an appearance of the classic “heart” shape
Cysts of the incisive papilla
Incisive papilla cyst
Is a soft tissue cyst (no bone involvement) located in
the same area as the Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
on the midline of the anterior hard palate
between and apical to the central incisors
. They may be symptomatic or asymptomatic and usually are not seen radiographically.
some consider them to be uncommon variants of the nasopalatine duct cysts
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Treatment
- surgical excision
- recurrence is rare
What is this radiographic finding?

Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
✎This person is edentulous
✎ an inverted pear shape
✎The nasal spine is superimposed
on your radiolucency ► a heart shape
What is this radiographic finding?
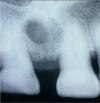
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
✎Between the roots of the two teeth, a well circumscribed
radiolucency, not showing any changes to the adjacent structures
✎could be an enlargement of the incisive canal due to variation in size ~ early lesions can be hard to diagnose
✎the treatment in such cases: a follow up with another radiograph in six months to see if there’s been any change in size
✎ No surgical intervention until you see the cyst expanding
What is this oral finding?

This is showing you the how the
papilla can be enlarged if it’s only
in soft tissue or if there’s a partial
soft tissue partial bone expansion
Nasopalatine Duct Cyst
Median Palatine Cyst
is
a variant of which cyst?
nasopalatine duct cyst
- it represents a more posteriorly placed nasopalatine duct cyst
- ~ It’s probably due to some sort of anatomic variation in the patients; that their palatine duct is just placed more posteriorly
- So instead of being between the roots of these two teeth, it’s placed more posteriorly
What is this radiographic finding?

Median Palatine Cyst
Median Mandibular Cyst
- A controversial cysts whose existence is questioned ~ similar to the globulomaxillary cyst
■ Originally thought to arise from the fusion of the “halves” of the mandible, but current embryology finds that
the mandible forms from a single bilobed process, therefore, no epithelial remnants would be found
■ Now, it is thought that cysts in this area represent odontogenic cysts or tumors
-
Median Mandibular Cyst is a term used to describe a cyst in a particular anatomic location not a definitive diagnosis
- ~ It is other lesions that occur in that particular location
- The Anterior Mandible
Is this Median Mandibular Cyst
Or something else

Remember
Median Mandibular Cyst is a term used to describe a cyst in a anterior mandible not a definitive diagnosis
So, this turned out to be an early ameloblastoma. It wasn’t a cyst
The lesion radiolucency in the anterior mandible and again
Surgical Ciliated
Cyst of the Maxilla
Etiology
■ Occurs after trauma or sinus surgery (iatrogenic - reactive not neoplastic)
Surgical Ciliated
Cyst of the Maxilla
Formation
■a portion of the sinus lining is separated from the sinus and forms an epithelial lined cavity in bone
■ Cavity fills with mucin produced by the mucous cells of the cyst lining
■ These cysts enlarge as the intraluminal pressure increases, causing destruction of bone
Surgical Ciliated
Cyst of the Maxilla
occurs frequently
after
which procedures?
- after a Caldwell-Luc procedure
- sometimes with difficult maxillary extractions
In which country Surgical Ciliated
Cyst of the Maxilla
are reported with higher frequency ?
Japan
What is this radiographic finding?

Surgical Ciliated
Cyst of the Maxilla
In this premolar shot (middle image) you can see a well-circumscribed lesion
✎Because the maxillary sinus is radiolucent, it almost looks like this is radiopaque but it’s not
✎ If you did a CBCT you would see that it’s an empty space within the bone of the maxilla. It’s not actually radiopaque


