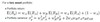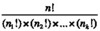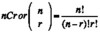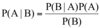Probability Concepts Flashcards
(78 cards)
Arrange in proper direction following terms
Random Variable , Outcome , Event,
Random Variable
What is a random variable?
Random variable is an uncertain quantity/number.
What is an Outcome?
Outcome is an observed value of a random variable.
What is an Event?
Event is a single outcome or a set of outcomes.
What is an Mutually Exclusive Event?
Mutually exclusive events are events that cannot both happen at the same time.
What is an Exhaustive Event?
Exhaustive events are those that include all possible outcomes.
What are the two defining properties of probability and distinguish among empirical, subjective, and a priori probabilities?
- The probability of an event is between 0 and 1.
- A set of events that is mutually exclusive and exhaustive, the sum of the probabilities are the sum of 1.
What is a subjective probability?
Subjective probability is the least formal method of developing probabilities and involves the use of personal judgment.
What is empirical probability?
Empirical probability is analyzing past data.
What is priori probability?
Priori probably uses a formal reasoning and inspection process.
What are the odds of rolling a 1 on a 6 sided die?
1 to 5
What are the odds of not rolling a 1 on a 6 sided die?
5 to 1
Probability of Odds Or Probability of Occurance
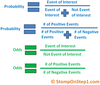
What is Unconditional Probability (Marginal Probability) ?
Unconditional probability refers to the probability of an event regardless of the past or future occurrence of other events.
What is Conditional Probability?
Conditional probability is one where the occurrence of one event affects the probability of the occurrence of another event.
The key word to watch for here is “given”.
Explain the multiplication rule of probability?
P(AB) = P(A|B) x P(B)
The multiplication rule of probability is used to determine the joint probability of two events

Explain the addition rule of probability?
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB)
The additional rule of probability is used to determine the probability that at least one of the 2 events will occur

Explain the Total Probability Rule?
The total probability rule is uesd to determine the unconditional probability of an event,given conditional probabilities

What is joint probability?
Joint probability of two events is the probability that they will both occur.
We can calculate this from the conditional probability that A will occur ( a conditional probability) and the probability that B will occur (the unconditional probability of B) .
This calculation is sometimes refered to as the multiplication rule of probability .
P(AB) = P(A/B) X P(B)
What is the difference between a dependent and independent event?
Independent event does not have any influence on occurrences of others.
The definition of independent events can be expreseed in terms of conditional probabilities . Events A and B are independent if and only if :-
P(A/B) = P(A) or equivalently P(B/A) = P(B)
If this condition is not satified the events are dependent events .
Standard Deviation of 2 stock portfolio

Factorial Notation
Use when assignment of members of a group to an equal number of positions
Multiplication Rule of Probability
P(AB) - P(A | B) x P(B)
Used to determine the joint probability of two events.
Addition Rule or Probability
Used to determine the probability that at least one of two events will occur:
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB)