PNP Minimodule Review (39b - 42b) Flashcards
Bless Silinsky (181 cards)
What are the therapeutic uses for neostigmine?
Neostigmine = cholinesterase inhibitor
- Skeletal NMJ
- Treat myasthenia gravis
- Reverse a non-depolarizing blocker after surgery
- Autonomic (theoretically enhances transmission at the parasympathetic muscarinic receptor, but rarely used)
- Glaucoma therapy
- Treat urinary retention
- Treat GI stasis

Which adrenergic receptors are activated by epinephrine?
What are the effects?
Epinephrine acts on all adrenergic receptors
- α1 -> vasoconstriction
- α2 -> inhibition of cellular functions
- β1 -> stimulates the heart
- β2 -> relax smooth muscle
- Note: This effect is at odds with α1 vasoconstriction; α1 effect will prevail at high doses
- β3 -> relax smooth muscle

What kind of drug is clonidine?
What is it used for?
Clonidine is a selective alpha-2 agonist (adrenergic)
Inhibits sympathetic outflow from CNS to periphery
- Antihypertensive
- Treat opioid withdrawal
Note: applies to other -onidines

Which agent cleaves synaptobrevin?
What is it used for?
Botox B
Used to treat muscle spasms in the neck (cervical dystonia)
What is the mechanism of rocuronium?
Nondepolarizing blocker at the NMJ
(post-synaptic agent)
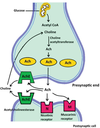
What enzyme degrades ACh in the NMJ?
Cholinesterase
Which agent cleaves SNARE SNAP-25? What is the effect?
Botox A -> Reduced muscle contraction
- Cleaves SNARE SNAP-25 near synaptotagmin’s Ca2+ binding site
- -> If synaptotagmin cannot bind Ca2+, the vesicle cannot release ACh into the nerve terminal
- -> Muscle twitch not initiated

What kind of drug is physostigmine?
What is it used for?
Reversible Cholinesterase inhibitor (indirect-acting parasympathomimetic)
Atropine poisoning
(Not a good antidote for irreversible anti-ChE poisioning!)
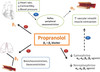
What are the contraindications for propranolol?
- Asthma
- Causes vasoconstriction and bronchoconstriction
- Diabetes
- Propranolol masks signs of hypoglycemia and decreases glycogenolysis
How is anticholinesterase toxicity treated?
Anticholinesterase toxicity is due to nerve gas or insecticide poisoning
- Decontaminate the patinet
- Give Atropine - blocks excessive muscarinic activity (autonomic)
- Give 2-PAM (or other -oxine) - reactivates ChE (skeletal muscle)
- Lifts the phosphoryl group from ChE, must be used quickly - Artificial respiration
- Anticonvulsants
Effect on the GI tract (muscle wall) of:
- Sympathetic stimulation:
- Parasympathetic stimulation:
- Sympathetic stimulation: Relaxation
- Not ideal to poop yourself during fight or flight response
- Parasympathetic stimulation: Contraction
What is the effect of inhibiting Uptake-1?
- Increased NE effect -> adrenergic receptor activation
- NE stays in the nerve terminal longer
- Tyramine has no effect
- Cannot get into the nerve terminal
Which drug is used to treat premature labor?
Terbutaline
(injectable beta-2 agonist)
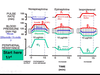
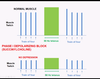
After a patient has received vecuronium or rocuronium as a neuromuscular blocker during surgery, what result from the “train of 4” indicates that:
- 80% of receptors are blocked?
- 90% of receptors are blocked?
- 80% of receptors are blocked = 2/4 twitches
- Twitch, twitch, no, no
- 90% of receptors are blocked = 1/4 twitches
- Twitch, no, no, no
What is the general effect of alpha-2 receptors in the CNS?
Alpha-2 activation reduces sympathetic tone
Example: Clonidine in the CNS activates alpha-2 receptors ->
- Decreased beta-1 action in the heart
- Decreased release of of NE from nerve terminal sthat innervate the heart
- Decreased alpha-1 vasoconstriction in the blood vessels

What kind of drug is propranolol?
What is it used for?
Nonselective beta-1 and beta-2 blocker
Also blocks renin release
Used to treat:
- Hypertension
- Arrhythmia
- Angina
- Pheochromocytoma
- Stage fright
- Prophylaxis for migraine headaches
- Acute phase of thyrotoxicosis
Which anticholinergic is used for anti-ChE poisoining?
Atropine
What are the autonomic responses to tactile or visual sexual stimulation?
Parasympathetic response
Erection and mucous secretion (both male and female)
How is NE (sympathetic) signaling terminated?
Reuptake into the nerve terminal by Uptake 1
- High affinity, low capacity
- Inhibited by tricyclic antidepressants, cocaine, ritalin
Alternative pathway: reuptake into the effector cell
- Low affinity, high capacity
Which drugs may be used for intubation in the early stage of anesthesia?
Succinylcholine (depolarizing)
Rocuronium (nondepolarizing)
List the components of the fusion machine
- 3 SNARE proteins that anchor the vesicle to the nerve plasma membrane
- Syntaxin (Plasma membrane)
- SNAP-25 (Plasma membrane)
- Synaptobrevin (Vesicular)
- One Ca2+ sensing protein
- Synaptotagmin (Vesicular)
What kind of drug is dobutamine?
What is it used for?
Selective Beta-1 agonist
Low doses selectively increase the force of cardiac contraction without increasing heart rate
- Acute heart failure
- Increase cardiac output
- Bridge to heart transplant
- Stress EKG
- High doses increase HR for patients who cannot exercise
What kind of drug is phentolamine?
What is it used for?
Nonselective reversible alpha blocker
- Treat hypertension:
- Crisis due to tyramine/MAO inhibition
- Paroxysms in pheochromocytoma
(Competitive antagonist)
Describe the differences in observed muscle twitches with depolarizing vs. nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers
- Depolarizing blocker
- Smaller amplitude, but no decline with sustained stimulation
- Nondepolarizing blocker
- Neuromuscular depression: repetitive stimulation results in progressive decline in twitch amplitude