89b - Limbic System Flashcards
A patient with a history of alcohol use disorder is explaining to you that they are late for their appointment because there was a bank robbery that they were stuck in on their way to the doctor. You know that this is unlikely, so you order a brain MRI.
Imaging shows increased signal intensity in the area of the mamillary bodies
How would you treat this patient?
Give thiamine
- Confabulation, spurious answers to questions, damage to mamillary bodies all support thiamine deficiency
- Thiamine deficiency is common in people with alcohol use disorder
Recall:
- Wernicke portion (acute)
- Ataxia
- Eye movement abnormalities
- Korsakoff portion
- Anterograde and retrograde amnesia
- Poor judgement, initiative, impulse controle
- Confabulation, spurious answers to questions
Technically, you give thiamine to prevent the Korsakoff portion, but it makes sense that even if that is there you should probably still supplement with thiamine?
What are the 4 main functions of the limbic system?
HOME
- Homeostasis (Hypothalamus)
- Olfaction (Olfactory cortex)
- Memory (Hippocampal formation)
- Emotions and Drives (Amygdala)
Stimulation of the amygdala will result in which behaviors/moods?
Fear
Anxiety
Rage
Aggression
Describe the structure of the hippocampus
Which sectors are most susceptible to ischemia?
- Divided into sectors CA1, CA2, CA3, CA4
- CA1 and CA2 are the Sommer Sector: most susceptible to ischemia

List the sructures in the hippocampal formation
- Dentate gyrus
- Input structure for the hippocampal formation
- Hippocampus
- Subiculum
Which receptors are targeted by limbic encephalitis?
What is the result?
NMDA receptors
- Cognitive impairment
- Disordered perception
- Mood changes
- Sleep distrubances
- Seizures
Which vitamin deficiency causes Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome?
Which brain structures are damaged?
What are the symptoms?
Thiamine deficiency
Mamillary bodies (bilateral necrosis)
- Wernicke portion (acute)
- Ataxia
- Eye movement abnormalities
- Korsakoff portion
- Anterograde and retrograde amnesia
- Poor judgement, initiative, impulse controle
- Confabulation, spurious answers to questions
What is the result of a bilateral hippocampal legion?
Anterograde amnesia
(No new memories can be formed)
This is what happened to patient HM
Which part of the brain is damaged in Alzheimer’s disease?
What is the result?
Parts of the Papez circuit
- Patients have impairment in learning new memories
- Difficulty recalling the names of people and objects
What is the function of the Papez Circuit?
Connects the cortex to the hypothalamus
It is the “anatomic substrate” for the convergence of cognitive activities, emotional experiences, and expression
List the steps in the pathway thorugh the paralymbic cortex
- Cingulate gyrus
- Paraolfactory gyrus
- Orbital-Frontal cortex
- Insula
- Uncus
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Back to cingulate
What is the function of the hippocampus?
Converts short term (up to 60 min) into long-term memory
Bilateral hippocampal lesion -> anterograde amnesia
Which area of the brain is most likely to be affected by HSV1 encephalitis?
Limbic cortex
- Can damage the hippocampi bilaterally, resulting in profound memory deficits
If the limbic system is damaged, what functions might be lost?
HOME
- Homeostasis (Hypothalamus)
- Olfaction (Olfactory cortex)
- Memory (Hippocampal formation)
- Emotions and Drives (Amygdala)
List the steps in the Papez circuit
- Parahippocampus (Entorhinal cortex)
- -> Perforant pathway -> dentate
- -> Alvear pathway
- Hippocampus
- Fornix
- Mammillary bodies
- -> mamillothalamic tract
- Thalamus
- -> internalcapsule
- Cingulate
- Back to the parahippocampal gyrus
Function: connect cortex to hypothalamus; the cortex sends inputs at each step
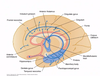
List the 5 components of the limbic system
- Limbic lobe
- Parahippocampal gyrus
- Cingulate gyrus
- Subcallosal gyrus
- Amygdala
- Hippocampal formation
- Olfactory cortex
- Hypothalamus

Lesions in which areas can result in anterograde amnesia?
- Bilateral hippocampus
- Bilateral fornix
- Other bilateral damages in the archicortex
- Old part of the limbic system
A lesion in the medial amygdala will result in which behaviors?
Anorexia
Hypersexuality
What is the most common symptom of damage to the limbic system?
Anterograde amnesia
- May be caused by trauma, vitamin deficiency, HSV1, autoimmune
- Takeaway: there are many things that can damage the limbic system, resulting in anterograde memory deficits
What is the function of the paralimbic cortex?
Connects the assoication cortex and the limbic system
- Converts multimodal experience into memory
A lesion in the lateral amygdala will result in what behavior?
Bulimia (unrestrained eating)
What is the function of the hippocampal formation
Short term and long term memory
Which structure serves as the input for the hippocampal formation?
Dentate gyrus


