Brain: How it grows and works (43b - 53b) Flashcards
Including what each part of the brain does (89 cards)
Which efferent pathway is involved in generating movement?
Corticostriate
Which MRI technique is used to evaluate contrast enhancement?
T1
- Great anatomic detail, but less sensitive to pathology
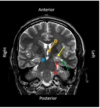
Occlusion of which artery leads to contralateral motor and sensory deficits in the lower limb?
Anterior cerebral artery

What is the most medial aspect of the temporal lobe?
The uncus of the temporal lobe
Clinical significance: swelling can compress the oculomotor nerve

A
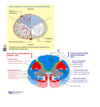
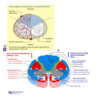
- Loss of motor function: cortical spinal tract bilaterally
- Loss of Pain and temperature: loss of both spinothalamic tracts
- Preservation of other senses because posterior column is intact
Which areas of the brain are supplied by the posterior cerebral artery?
Occlusion leads to what deficits?
- Occipital lobe
- Inferior temporal lobe
- Posterior limb of the internal capsule
Loss of contralateral visual fields, color vision, visual/spatial problems
(Minimal motor or sensory deficits)

What neurotransmitter is synthesized in the raphe nuclei?
Serotonin
The outermost layer of the neocortex is layer ___
This layer developes [latest/earliest]
The outermost layer of the neocortex is layer 1
This layer developes latest
- Layer 6 is the innermost layer and develops first
- Neurons of subsequent layers prolifereate, differentiate, and then migrate from deep to superficial
- Layer 6 neurons are the oldest, while layer 1 neurons are the youngest
At what gestational age can 6 cortical layers be identified?
18 weeks post conception
What makes up a “disynaptic pathway?”
Sensory neuron + interneuron + motor neuron
A 63yo man with a history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes presents with acute onset of weakness and numbness of the right face and arm, global aphasia, and a left gaze palsy.
He is able to raise his right leg.
A stroke due to occlusion of what artery might cause these symptoms?
Middle cerebral artery
- Supplies the lateral surface of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
- Language areas
- Motor cortex
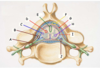
A lateral lesion in the brainstem, as occurs in the lateral medullary syndrome, will damage which of the following cranial nerve nuclei?
- Hypoglossal nucleus
- Trochlear nucleus
- Abducens nucleus
- Oculomotor nucleus
- Spinal nucleus of V
E. Spinal nucleus of V
- A lateral lesion will damage sensory nuclei
- All other options are motor nuclei
Which cortical layer receives thalamic input?
Which cortical layer sends output back to the thalamus?
Which cortical layer receives thalamic input? Layer IV
Which cortical layer sends output back to the thalamus? Layer VI
What does fMRI measure?
What is this technique used for?
fMRI measures deoxyhemoglobin
- Helps us assess which areas of the brain are using the most oxygen
- It is an indirect measurement of electrical activity in the brain
- Used to determine which areas are used in different functions so they can be avoided during surgery
A 21 year old man with a history of precocious puberty presents for evaluation of transient episodes characterized by uncontrolled laughing?
Which image best fits this description?

iii
- Hypothalamus
- Produces hormones involed in endocrine axes

Which structures are contained in the tegmentum of the midbrain?
- Red nucleus
- Principle sensory nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- Reticular formation
- Substantia nigra
At what level of the brainstem is the decussation of the pyramids?
Spinomedullary junction

What is the etiology of Rett syndrome?
Disorder of synaptogenesis
The [area of the brain] is the relay from the brainstem to the cerebral cortex
The diencephalon is the relay from the brainstem to the cerebral cortex
Contains the thalamus
Which nerve exits throught the intervertebral foramen between the C6 and C7 vertebrae?
The C7 spinal nerve
Although there are seven cervical vertebrae (C1-C7), there are eight cervical nerves C1–C8. C1–C7 emerge above their corresponding vertebrae, while C8 emerges below the C7 vertebra. Elsewhere in the spine, the nerve emerges below the vertebra with the same name (T1 nerve emerges below T1 vertebrae, etc)
What neurotransmitter is synthesized in the ventral area of the tegmentum?
Dopamine
CSF appears bright in [T1/T2] weighted MRIs
CSF appears bright in T2 weighted MRIs
Loss of pain and temperature sensation on the right side of the face might be due to a lesion in which tract?
Right spinal tract of V
Trigeminal lemniscus carries proprioception, touch, pressure, vibration
(Aka right trigeminothalamic tract)
A 60 y.o. male presents with dysphagia, decreased coordination (falling to left side), and left lower facial droop after a bicycle accident in which he hyperextended his neck. On imaging, he is found to have a stroke.
Which brain structures are most likely affected?
Left cerebellum
(likely medial/intermediat stuructures if posture is affected)