Physiological Labour Flashcards
When is birth classed as ‘pre-term’ labour?
Labour that occurs before the 37th week of gestation
When is expulsion of the products of conception classed as sponaneous abortion (miscarriage)?
If this occurs before 24 weeks
What processes are required to expel a fetus?
- Creation of a birth canal
- Release of structures which retain the fetus in utero
- Elargement and realignment of the cervix and vagina
- Expulsion of fetus
- Expulsion of placenta and chages to minimise blood loss
What are the 3 stages of labour?
- Stage 1- onset of regular contractions until the cervix is fully dilated
- Stage 2- When the cervix is fully dilated untl the birth of the baby
- Stage 3- From birth of the baby to the delivery of the placenta and membranes and bleeding is controlled
What is the ‘lie’ of a fetus? What is the most common lie?
The relationship of the long axis of the fetus to the long axis of the uterus
The most common lie is longitudinal

What is the ‘presentation’ of the fetus?
Describes which part of the fetus is adjacent to the pelvic inlet
Presenting part may be the head- cephalic or breeched (podalic) which is feet 1st

What diameter does the cervix need to be in order for the fetus to pass through?
10cm
What are the boundaries of the pelvic inlet?
- Posterior - the sacral promontory
- Lateral- the ilio-pectinal line
- Anterior - the superior pubic rami and upper margin of the pubic symphysis
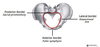
What is the true diameter of the pelvic inlet?
~11 cm
What happens to the pelvic ligaments before birth?
Pelvic ligaments relax due to high progesterone, allows expansion to occur
What is ‘cervical ripening’ / ‘softening’
A marked reduction in collagen and an increase in glycosaminoglycans which decrease the aggregation of collagen fibres so collagen bundles loosen
There is an influx of inflammatory cellls and increased NO output triggered by prostoglandins E2 and F2 alpha
What 2 changes happen to the cervix during labour?
- Dilation
- Effacement - thinning of the cervix

What happens to the uterine smooth muscle during pregnancy?
- Myometrium gets thicker due to an increased cell size and glycogen depositon
How is contraction of the myometrium co-ordinated?
- Action potentials spread by gap juctions cell to cell for co-ordinated contraction over the myometrium
- Some cells can spontaneously depolarise and act as pacemakers
What are Braxton- Hicks contractions?
Contractions in the late stage of pregnancy that aren’t foreceful enough to effect the fetus
Generates as amplitude of contractions increases
Which 2 hormones are involved in increasing the frequency and force of the contractions and how?
Prostaglandins: enhances the release of Calcium from intracellular stores
Oxytocin: from posterior pituitary lowers the threshold for triggering action potentials. Myometrium becomes more sensitive to oxytocin as receptors are upregulated
Explain the Ferguson Reflex during labour
An example of positive feedback
- Fetal head pushes on the cervix
- Oxytocin release from posterior pituitary
- Causes more contractions
- Causes fetal head to push onto cervix making contractions more forceful & frequent
- Will continue until the baby is delivered

Explain the principle of brachystasis
During labour, uterine smooth muscle fibres will shorten with each contraction but do not fully relax
Causes the uterus to progressively shorten pushing the presenting part into the birth canal

How is pregnancy initiated in humans?
Unclear situation
However, medically prescribed prostaglandins will induce labour
Why does the babies heart rate need to be carefully monitored during labour?
- Foreful uterine contractions can temporarily reduce placental blood flow → reducing O2 supply to the fetus
- May cause brief drops in fetal heart rate
- If reductions are larger greater dips in HR occur showing the fetus is distressed
How long does the second stage of labour last?
1 hour in multiparous women
Up to 2 hours in primigravida (1st pregnancy)
Give the steps of the 2nd stage of labour
- Descended head flexes as it meets the pelvix floor, reducing the diameter of presentation
- Internal rotation of fetus
- Sharply flexed head descends to the vulva, stretching vagina and perineum
- Head is delivered ‘crowing’, as it emerges it rotates back to it’s orginal postion and extends
- Shoulders rotate followed by the head, shoulders are delivered rapidly followed by the rest of the fetus

What is the typical legnth of the 3rd stage of labour?
10 minutes
How is uterine bleeding stopped after placental delivery?
The uterus contracts and compresses blood vessels to reduce bleeding
Oxytocin can be given to help
How is the health of a neonate assessed after delivery?
APGAR score
Assesses baby on Appearance, Pulse, Grimace, Activity and Respiration at delivery and 5 mins after
The higher the score the healthier the baby
What are the Power, Passage and Passenger?
The Power = myometrium contraction and progressive shortening
The Passage = getting through the bony pelvis and soft tissues
The Passenger = the size and presentation of the fetus in labour
Failure to progress into labour can come from any of these factors


